在线视频:尚硅谷2024最新Java入门视频教程(下部)-API 尚硅谷2024新版Java基础 https://gitee.com/an_shiguang/learn-java
重点内容:
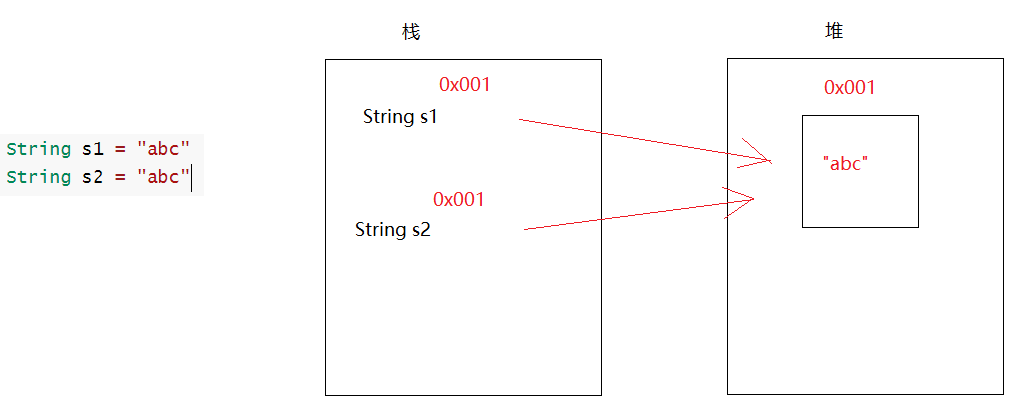
String String介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1. 概述:String 类代表字符串2. 特点: a.Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例(对象)实现 凡是带双引号的,都是String的对象 String s = "abc" "abc" 就是对象;String就是对象的数据类型;s就是对象名 b.字符串是常量,它们的值在创建之后不能更改 String s = "hello" s+="world" -> 会产生新对象 c.String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享 String s1 = "abc" String s2 = "abc"
String的实现原理 1 2 3 4 5 1. jdk8的时候:String底层是一个被final 修饰的char 数组-> private final char [] value;2. jdk9开始到之后:底层是一个被final 修饰的byte 数组-> private final byte [] value; 一个char 类型占2 个字节 一个byte 类型占1 个字节 -> 省内存空间
1 字符串定义完之后,数组就创建好了,被final 一修饰,数组的地址值直接定死
String的创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1. String() -> 利用String的无参构造创建String对象2. String(String original) -> 根据字符串创建String对象3. String(char [] value) -> 根据char 数组创建String对象4. String(byte [] bytes) -> 通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String a.平台:操作系统 b.操作系统默认字符集:GBK GBK:一个中文占2 个字节 UTF-8 :一个中文占3 个字节 而且,中文对应的字节一般都是负数 代码在idea中写的,idea启动的时候,会自动加一个启动参数,此启动参数为UTF-8 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 5. 简化形式: String 变量名 = ""
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Demo02String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s1 = new String (); System.out.println(s1); String s2 = new String ("abc" ); System.out.println(s2); char [] chars = {'a' ,'b' ,'c' }; String s3 = new String (chars); System.out.println(s3); byte [] bytes1 = {97 ,98 ,99 }; String s4 = new String (bytes1); System.out.println(s4); byte [] bytes2 = {-97 ,-98 ,-99 }; String s5 = new String (bytes2); System.out.println(s5); byte [] bytes3 = {-28 ,-67 ,-96 }; String s6 = new String (bytes3); System.out.println(s6); String s7 = "abc" ; System.out.println(s7); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. String(char [] value, int offset, int count)->将char 数组的一部分转成String对象 value:要转String的char 数组 offset:从数组的哪个索引开始转 count:转多少个 2. String(byte [] bytes, int offset, int length)->将byte 数组的一部分转成String对象 bytes:要转String的byte 数组 offset:从数组的哪个索引开始转 length:转多少个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Demo03String { public static void main (String[] args) { char [] chars = {'a' ,'b' ,'c' ,'d' ,'e' ,'f' }; String s1 = new String (chars,1 ,3 ); System.out.println(s1); byte [] bytes = {97 ,98 ,99 ,100 ,101 }; String s2 = new String (bytes,0 ,2 ); System.out.println(s2); } }
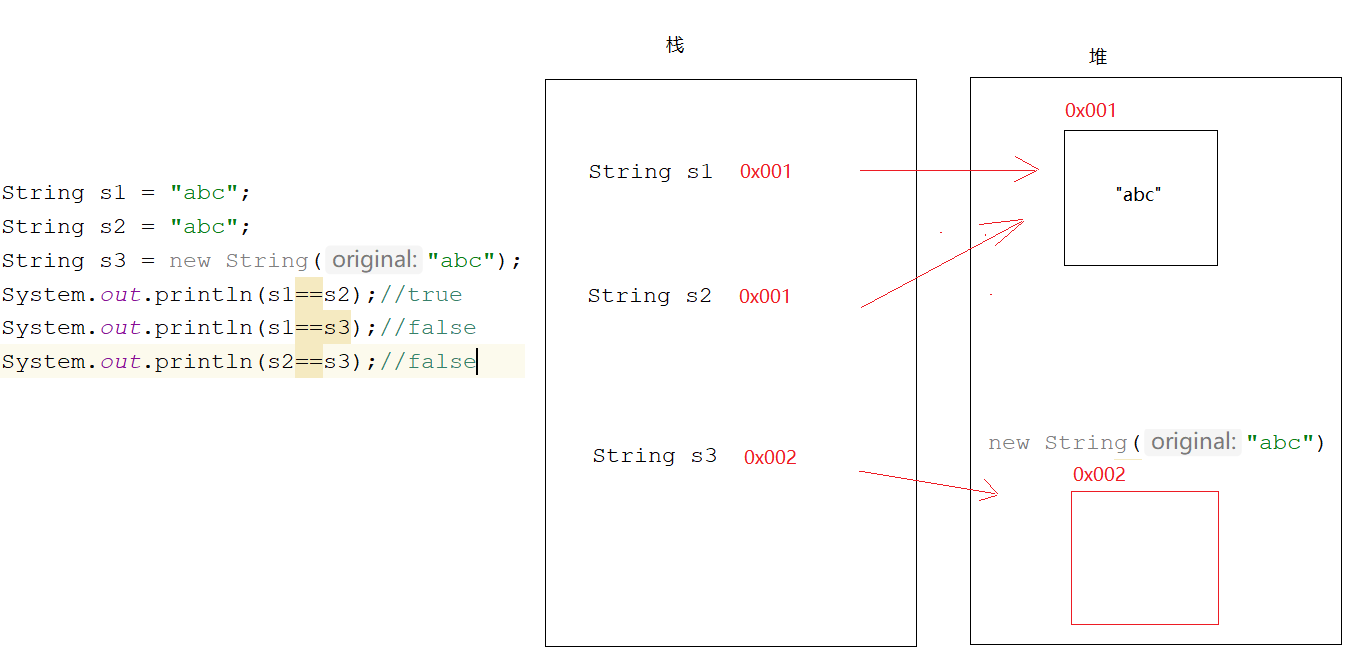
String 面试题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo04String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s1 = "abc" ; String s2 = "abc" ; String s3 = new String ("abc" ); System.out.println(s1==s2); System.out.println(s1==s3); System.out.println(s2==s3); } }
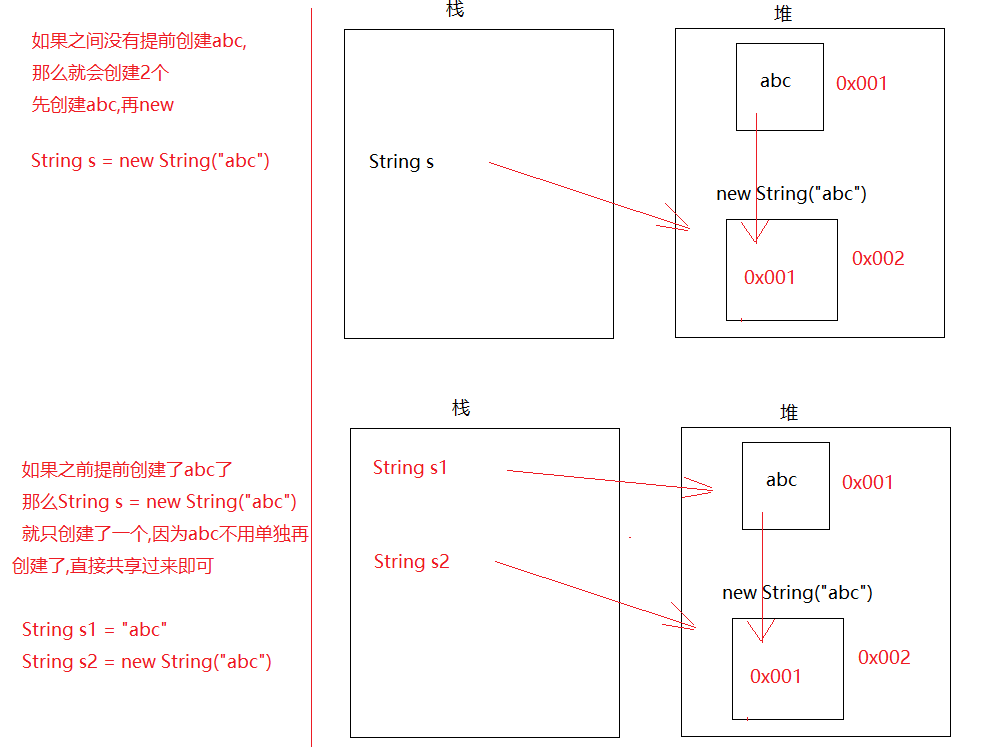
1 2 3 4 5 问1 :String s = new String ("abc" )共有几个对象? 2 个 一个new 本身 一个是"abc" 问2 :String s = new String ("abc" )共创建了几个对象? 1 个或者2 个 就看abc有没有提前创建出来了
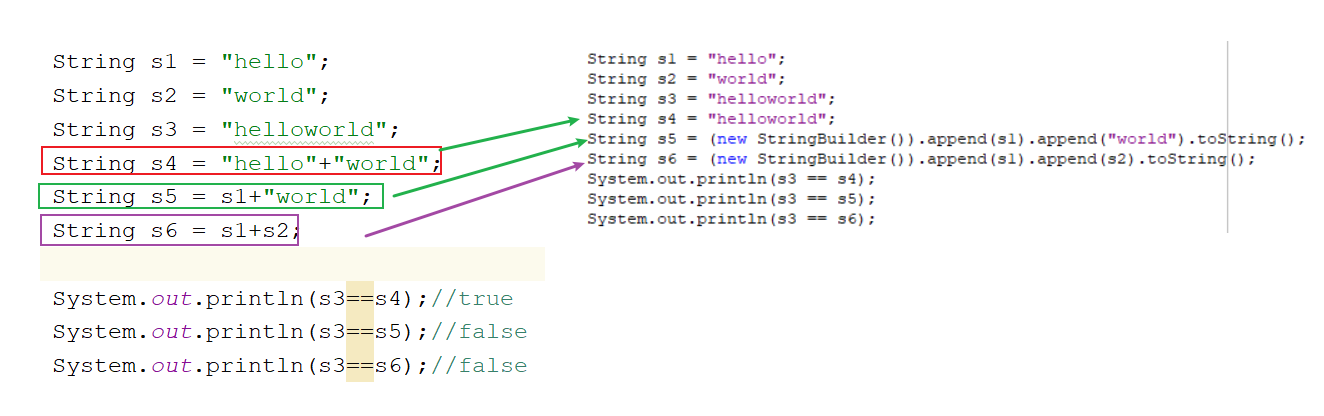
字符串常见问题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Demo05String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s1 = "hello" ; String s2 = "world" ; String s3 = "helloworld" ; String s4 = "hello" +"world" ; String s5 = s1+"world" ; String s6 = s1+s2; System.out.println(s3==s4); System.out.println(s3==s5); System.out.println(s3==s6); } }
1.字符串拼接,如果等号右边是字符串字面值拼接,不会产生新对象
2.字符串拼接,如果等号右边有变量参数拼接,会产生新字符串对象
String的方法 判断方法 1 2 boolean equals (String s) -> 比较字符串内容boolean equalsIgnoreCase (String s) -> 比较字符串内容,忽略大小写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Demo01String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s1 = "abc" ; String s2 = new String ("abc" ); String s3 = "Abc" ; System.out.println(s1==s2); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); System.out.println("=========================" ); String s4 = "123" ; String s5 = "一二三" ; System.out.println(s4.equalsIgnoreCase(s5)); String s6 = "壹贰叁" ; System.out.println(s5.equalsIgnoreCase(s6)); } }
练习1 1 2 3 4 5 已知用户名和密码,请用程序实现模拟用户登录。总共给三次机会,登录成功与否,给出相应的提示 步骤: 1. 先定义两个字符串,表示注册过的用户名和密码 2. 创建Scanner对象,键盘录入用户名和密码 3. 比较,如果输入的用户名和密码跟已经注册过的用户名和密码内容一样,就登录成功,否则就登录失败
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Demo02String { public static void main (String[] args) { String username = "root" ; String password = "123" ; Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { System.out.println("请您输入用户名:" ); String name = sc.next(); System.out.println("请您输入密码:" ); String pwd = sc.next(); if (name.equals(username) && pwd.equals(password)) { System.out.println("登录成功" ); break ; } else { if (i == 2 ) { System.out.println("账号冻结" ); } else { System.out.println("登录失败!" ); } } } } }
equals()防止空指针的两个写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import java.util.Objects;public class Demo03String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s = null ; String s1 = null ; String s2 = "abc" ; method01(s1, s2); } private static void method01 (String s1, String s2) { if (Objects.equals(s1, s2)) { System.out.println("是abc" ); } else { System.out.println("不是abc" ); } } private static void method (String s) { if ("abc" .equals(s)) { System.out.println("是abc" ); } else { System.out.println("不是abc" ); } } }
获取功能 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int length () -> 获取字符串长度String concat (String s) -> 字符串拼接,返回新串儿 char charAt (int index) -> 根据索引获取对应的字符int indexOf (String s) -> 获取指定字符串在大字符串中第一次出现的索引位置String subString (int beginIndex) -> 截取字符串,从指定索引开始截取到最后,返回新串儿 String subString (int beginIndex,int endIndex) -> 截取字符串,从beginIndex开始到endIndex结束 含头不含尾,返回新串儿
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Demo04String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s1 = "abcdefg" ; System.out.println(s1.length()); System.out.println(s1.concat("haha" )); System.out.println(s1.charAt(0 )); System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a" )); System.out.println(s1.substring(3 )); System.out.println(s1.substring(1 ,6 )); } }
练习2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Demo05String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s = "abcdefg" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { System.out.println(s.charAt(i)); } } }
转换功能 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. char [] toCharArray() -> 将字符串转成char 数组2. byte [] getBytes() -> 将字符串转成byte 数组3. String replace (CharSequence c1,CharSequence c2) -> 替换字符 CharSequence->String的接口 4. byte [] getBytes(String charsetName) -> 按照指定的编码将字符串转成byte 数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;public class Demo06String { public static void main (String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String s = "abcdefg" ; char [] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < chars.length; i++) { System.out.println(chars[i]); } System.out.println("===============" ); byte [] bytes = s.getBytes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < bytes.length; i++) { System.out.println(bytes[i]); } System.out.println("===============" ); System.out.println(s.replace("a" , "z" )); System.out.println("===============" ); byte [] bytes1 = "你好" .getBytes("GBK" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < bytes1.length; i++) { System.out.println(bytes1[i]); } } }
练习4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 键盘录入一个字符串,统计该字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数(不考虑其他字符) 步骤: 1. 创建Scanner对象,键盘录入 2. 定义三个变量,用来统计 3. 调用next方法录入一个字符串,遍历字符串,将每一个字符拿出来 4. 统计大写字母 A-Z -> 65 -90 比如:B -> 66 -> 在65 -90 之间,证明就是大写字母 5. 统计小写字母 a-z -> 97 -122 比如:b -> 98 -> 在97 -122 之间,证明就是小写字母 6. 统计数字: 0 -9 -> 48 -57 比如:字符1 -> 49 -> 在48 -57 之间,证明就是数字 7. 将统计结果打印出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import java.util.Scanner;public class Demo07String { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int big = 0 ; int small = 0 ; int number = 0 ; String data = sc.next(); char [] chars = data.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < chars.length; i++) { char num = chars[i]; if (num >= 'A' && num <= 'Z' ) { big++; } if (num >= 'a' && num <= 'z' ) { small++; } if (num >= '0' && num <= '9' ) { number++; } } System.out.println("大写有" + big + "个" ); System.out.println("小写有" + small + "个" ); System.out.println("数字有" + number + "个" ); } }
分割功能 1 2 1. String[] split(String regex)->按照指定的规则分割字符串 注意:regex写的是正则表达式 -> . 在正则表达式中代表任意一个字符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo08String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s = "abc,txt" ; String[] split = s.split("," ); for (int i = 0 ; i < split.length; i++) { System.out.println(split[i]); } System.out.println("===============" ); String s2 = "haha.hehe" ; String[] split1 = s2.split("\\." ); for (int i = 0 ; i < split1.length; i++) { System.out.println(split1[i]); } } }
String其他方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. boolean contains (String s) -> 判断老串儿中是否包含指定的串儿2. boolean endsWith (String s) -> 判断老串儿是否以指定的串儿结尾3. boolean startsWith (String s) -> 判断老串儿是否以指定的串儿开头4. String toLowerCase () -> 将字母转成小写5. String toUpperCase () -> 将字母转成大写6. String trim () -> 去掉字符串两端空格
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Demo09String { public static void main (String[] args) { String s = "abcdefg" ; System.out.println(s.contains("a" )); System.out.println(s.endsWith("g" )); System.out.println(s.startsWith("a" )); System.out.println("ADbcda" .toLowerCase()); System.out.println("dafadRWERW" .toUpperCase()); System.out.println(" hadfhad hdsfha sfhdsh " .trim()); System.out.println("==================" ); System.out.println(" hadfhad hdsfha sfhdsh " .replace(" " ,"" )); } }
StringBuilder类 StringBuilder的介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1. 概述:一个可变的字符序列,此类提供了一个与StringBuffer兼容的一套API,但是不保证同步(线程不安全,效率高)2. 作用:主要是字符串拼接3. 问题: a.刚讲完String,String也能做字符串拼接,直接用+即可,但是为啥还要用StringBuilder去拼接呢? b.原因: String每拼接一次,就会产生新的字符串对象,就会在堆内存中开辟新的空间,如果拼接次数多了,会占用内存,效率比较底 StringBuilder,底层自带一个缓冲区(没有被final 修饰的byte 数组)拼接字符串之后都会在此缓冲区中保存,在拼接的过程中,不会随意产生新对象,节省内存 4. StringBuilder的特点: a.底层自带缓冲区,此缓冲区是没有被final 修饰的byte 数组,默认长度为16 b.如果超出了数组长度,数组会自动扩容 创建一个新长度的新数组,将老数组的元素复制到新数组中,然后将新数组的地址值重新赋值给老数组 c.默认每次扩容老数组的2 倍+2 如果一次性添加的数据超出了默认的扩容数组长度(2 倍+2 ),比如存了36 个字符,超出了第一次扩容的34 ,就按照实际数据个数为准,就是以36 扩容
StringBuilder的使用 1 2 3 1. 构造: StringBuilder() StringBuilder(String str)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo01StringBuilder { public static void main (String[] args) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); System.out.println(sb); StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder ("abc" ); System.out.println(sb1); } }
1 2 3 4 常用方法: StringBuilder append (任意类型数据) -> 字符串拼接,返回的是StringBuilder自己 StringBuilder reverse () -> 字符串翻转,返回的是StringBuilder自己 String toString () -> 将StringBuilder转成String-> 用StringBuilder拼接字符串是为了效率,为了不占内存,那么拼完之后我们后续可能会对拼接好的字符串进行处理,就需要调用String中的方法,所以需要将StringBuilder转成String
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Demo02StringBuilder { public static void main (String[] args) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); StringBuilder sb1 = sb.append("张无忌" ); System.out.println(sb1); System.out.println(sb); System.out.println(sb==sb1); System.out.println("==============" ); sb.append("赵敏" ).append("周芷若" ).append("小昭" ); System.out.println(sb); sb.reverse(); System.out.println(sb); String s = sb.toString(); System.out.println(s); } }
1 2 练习:键盘录入一个字符串,判断此字符串是否为"回文内容" 比如: abcba 上海自来水来自海上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.Scanner;public class Demo03StringBuilder { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); String data = sc.next(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (data); sb.reverse(); String s = sb.toString(); if (data.equals(s)) { System.out.println("是回文内容" ); } else { System.out.println("不是回文内容" ); } } }
练习 1 定义一个数组,以[元素1 , 元素2 , 元素3. .]的形式输出,用StringBuilder拼接
String:拼接字符串效率低,每拼接一次,都会产生一个新的字符串对象,耗费内存资源
StringBuilder和StringBuffer区别:
a.相同点:
用法一样,作用一样
b.不同点:
StringBuilder:拼接效率比StringBuffer高
线程不安全
StringBuffer:效率比较底,线程安全
拼接效率:StringBuilder>StringBuffer>String
String 总结 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 模块14 回顾: String: 1. 构造: String() String(String s) String(char [] chars) String(byte [] bytes) String(char [] chars,int offset,int count) String(byte [] chars,int offset,int count) 2. 判断方法: equals equalsIgnoreCase 3. 获取方法: length() concat(String s) charAt(int index) indexOf(String s) subString(开始索引) subString(开始索引,结束索引) -> 含头不含尾 4. 转换方法: toCharArray() getBytes() getBytes(String charsetName) replace(c1,c2) 5. 分割方法: split(String regex) 6. 其他方法: contains(String s) endsWith(String s) statsWith(String s) toLowerCase() toUpperCase() trim() StringBuilder: 1. append(任意类型数据) 2. reverse() 3. toString() 模块十五重点: 1. 会BigInteger和BigDecimal操作 2. 会Date和SimpleDateFormat的操作 3. 会System中的常用方法 -> 主要是数组复制 4. 会Arrays中的常用方法 5. 会利用包装类定义一个标准的javabean 6. 会包装类和String之间的转换
Math类方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 static int abs (int a) -> 求参数的绝对值static double ceil (double a) -> 向上取整static double floor (double a) ->向下取整static long round (double a) -> 四舍五入static int max (int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较大值 static int min (int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较小值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo01Math { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-10 )); System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.6 )); System.out.println(Math.floor(3.6 )); System.out.println(Math.round(3.6 )); System.out.println(Math.round(-2.8 )); System.out.println(Math.max(10 ,20 )); System.out.println(Math.min(10 ,20 )); } }
BigInteger BigInteger介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. 问题描述:我们操作数据,将来的数据有可能非常大,大到比long 还要大,这种数据我们一般称之为"对象" 2. 作用: 处理超大整数 3. 构造: BigInteger(String val) -> 参数的格式必须是数字形式 4. 方法: BigInteger add (BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigInteger BigInteger subtract (BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigInteger BigInteger multiply (BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigInteger BigInteger divide (BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigInteger
BigInteger使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.math.BigInteger;public class Demo02BigInteger { public static void main (String[] args) { BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger ("121212121212121212121212121212121212121" ); BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger ("121212121212121212121212121212121212121" ); System.out.println(b1.add(b2)); System.out.println(b1.subtract(b2)); System.out.println(b1.multiply(b2)); System.out.println(b1.divide(b2)); } }
int intValue() 将BigInteger转成int
long longValue() 将BigInteger 转成 long
BigInteger上限:42亿的21亿次方,内存根本扛不住,所以我们可以认为BigInteger无上限
BigDecimal类 BigDecimal介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 1. 问题描述:我们知道直接用float 或者double 做运算会出现精度损失的问题,所以将来设计到钱,我们就不能用float 或者double 直接做运算 2. 作用:主要是解决float 和double 直接做运算出现的精度损失问题 3. 构造方法: BigDecimal(String val) -> val必须要是数字形式 不建议使用 BigDecimal(double val),此构造方法的结果有一定的不可预知性 例如 new BigDecimal (0.1 ); 得到的结果是0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625 4. 常用方法: static BigDecimal valueOf (double val) -> 此方法初始化小数时可以传入double 型数据 BigDecimal add (BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigDecimal BigDecimal subtract (BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigDecimal BigDecimal multiply (BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigDecimal BigDecimal divide (BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigDecimal BigDecimal divide (BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode) divisor:除号后面的那个数 scale:指定保留几位小数 roundingMode:取舍方式 static int ROUND_UP -> 向上加1 static int ROUND_DOWN -> 直接舍去 static int ROUND_HALF_UP -> 四舍五入 5. 注意: 如果除不尽,会报错,出现运算异常
BigDecimal使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import java.math.BigDecimal;public class Demo03BigDecimal { public static void main (String[] args) { big03(); } private static void big03 () { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal ("3.55" ); BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal ("2.12" ); BigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2, 2 , BigDecimal.ROUND_UP); System.out.println("divide = " + divide); double v = divide.doubleValue(); System.out.println("v = " + v); } private static void big02 () { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal ("3.55" ); BigDecimal b2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(2.12 ); BigDecimal add = b1.add(b2); System.out.println("add = " + add); BigDecimal subtract = b1.subtract(b2); System.out.println("subtract = " + subtract); BigDecimal multiply = b1.multiply(b2); System.out.println("multiply = " + multiply); BigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2); System.out.println("divide = " + divide); } private static void big01 () { float a = 3.55F ; float b = 2.12F ; float result = a - b; System.out.println("result = " + result); } }
double doubleValue() 将此BigDecimal转成double
BigDecimal除法过时方法解决 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. 注意:如果调用的成员上面有一个横线,证明此成员过时了,底层会有一个注解@Deprecated 修饰,但是过时的成员还能使用,只不过被新的成员代替了,不推荐使用了 2. 方法: divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, RoundingMode roundingMode) divisor:代表除号后面的数据 scale:保留几位小数 roundingMode:取舍方式-> RoundingMode是一个枚举,里面的成员可以类名直接调用 UP:向上加1 DOWN:直接舍去 HALF_UP:四舍五入
1 2 3 4 5 6 private static void big04 () { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal ("3.55" ); BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal ("2.12" ); BigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2, 2 , RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.println("divide = " + divide); }
Date日期类 Date类的介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 概述:表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒2. 常识: a.1000 毫秒 = 1 秒 b.时间原点:1970 年1 月1 日 0 时0 分0 秒(UNIX系统起始时间),叫做格林威治时间,在0 时区上 c.时区:北京位于东八区,一个时区经度差15 度,时间相差一个小时,所以北京时间比时间原点所在时区时间差8 个小时 d.北京经纬度:东经116 北纬39.56 -> 温带大陆性季风气候 e.赤道 本初子午线(0 度经线)
Date类的使用 1 2 3 1. 构造: Date() -> 获取当前系统时间 Date(long time) -> 获取指定时间,传递毫秒值 -> 从时间原点开始算
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private static void date01 () { Date date1 = new Date (); System.out.println("date1 = " + date1); Date date2 = new Date (1000L ); System.out.println("date2 = " + date2); }
Date类的常用方法 1 2 1. void setTime (long time) -> 设置时间,传递毫秒值-> 从时间原点开始算2. long getTime () ->获取时间,返回毫秒值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private static void date02 () { Date date = new Date (); date.setTime(1000L ); System.out.println(date.getTime()); }
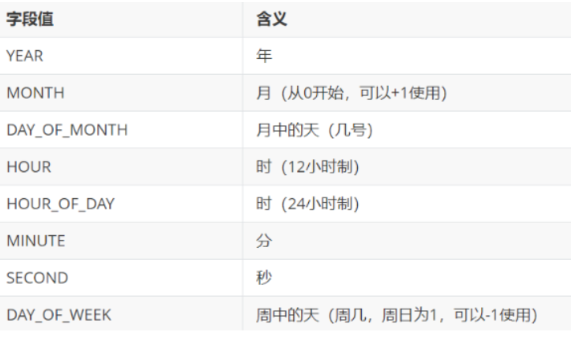
Calendar日历类 Calendar介绍 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. 概述:日历类,抽象类2. 获取:Calendar中的方法: static Calendar getInstance () 3. 月份对比: 国外: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 国内: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 常用方法: int get (int field) ->返回给定日历字段的值 void set (int field, int value) :将给定的日历字段设置为指定的值 void add (int field, int amount) :根据日历的规则,为给定的日历字段添加或者减去指定的时间量 Date getTime () :将Calendar转成Date对象 field:代表的是日历字段-> 年 月 日 星期等,都是静态的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date;public class Demo02Calendar { public static void main (String[] args) { calendar02(); } private static void calendar02 () { Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR); System.out.println("year = " + year); calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR,-1 ); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)); Date date = calendar.getTime(); System.out.println("date = " + date); } }
扩展方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void set (int year, int month, int date) -> 直接设置年月日需求:键盘录入一个年份,判断这一年是闰年,还是平年 步骤: 1. 创建Calendar对象 2. 创建Scanner对象,键盘录入一个年份 3. 调用set方法,传递年,月,日 set(年,2 ,1 ) -> 国外是0 -11 ,所以设置成2 月就是代表3 月 4. 将day减1 天(3 月1 日减1 天,就是2 月最后一天,知道2 月最后一天了,就知道是平年还是闰年了) 5. 获取day判断平年还是闰年,输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private static void calendar03 () { Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int year = sc.nextInt(); calendar.set(year,2 ,1 ); calendar.add(Calendar.DATE,-1 ); int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DATE); if (day==29 ){ System.out.println("闰年" ); }else { System.out.println("平年" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. 概述:日期格式化类2. 构造: SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) 3. pattern代表啥:代表的是我们自己指定的日期格式 字母不能改变,但是中间的连接符我们可以改变 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
时间字母表示
说明
y
年
M
月
d
日
H
时
m
分
s
秒
1 2 1. String format (Date date) -> 将Date对象按照指定的格式转成String 2. Date parse (String source) -> 将符合日期格式的字符串转成Date对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.text.ParseException;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;public class Demo03SimpleDateFormat { public static void main (String[] args) throws ParseException { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ); String time1 = sdf.format(new Date ()); System.out.println("time1 = " + time1); String time2 = "2000-10-10 10:10:10" ; Date date = sdf.parse(time2); System.out.println("date = " + date); } }
JDK8新日期类 LocalDate 本地日期 获取LocalDate对象 1 2 3 4 1. 概述:LocalDate是一个不可变的日期时间对象,表示日期,通常被视为年月日2. 获取: static LocalDate now () -> 创建LocalDate对象 static LocalDate of (int year, int month, int dayOfMonth) -> 创建LocalDate对象,设置年月日
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.time.LocalDate;public class Demo04LocalDate { public static void main (String[] args) { LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); System.out.println("localDate = " + localDate); LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2000 , 10 , 10 ); System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1); } }
LocalDateTime对象 1 2 3 4 5 1. LocalDateTime概述:LocalDateTime是一个不可变的日期时间对象,代表日期时间,通常被视为年 - 月 - 日 - 时 - 分 - 秒。 2. 获取:static LocalDateTime now () 创建LocalDateTime对象static LocalDateTime of (int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second) 创建LocalDateTime对象,设置年月日时分秒
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.time.LocalDateTime;public class Demo05LocalDateTime { public static void main (String[] args) { LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime); LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2000 , 10 , 10 , 10 , 10 , 10 ); System.out.println("localDateTime1 = " + localDateTime1); } }
获取日期字段的方法 : 名字是get开头 1 2 3 int getYear () ->获取年份int getMonthValue () ->获取月份int getDayOfMonth () ->获取月中的第几天
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private static void get () { LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); System.out.println(localDate.getYear()); System.out.println(localDate.getMonthValue()); System.out.println(localDate.getDayOfMonth()); }
设置日期字段的方法 : 名字是with开头 1 2 3 LocalDate withYear (int year) :设置年份 LocalDate withMonth (int month) :设置月份 LocalDate withDayOfMonth (int day) :设置月中的天数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private static void with () { LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.withYear(2000 ).withMonth(10 ).withDayOfMonth(10 ); System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1); }
日期字段偏移 1 2 设置日期字段的偏移量,方法名plus开头,向后偏移 设置日期字段的偏移量,方法名minus开头,向前偏移
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private static void plusAndMinus () { LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.minusYears(1L ); System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1); }
Period和Duration类 Period 计算日期之间的偏差 1 2 3 4 5 6 方法: static Period between (LocalDate d1,LocalDate d2) :计算两个日期之间的差值 getYears()->获取相差的年 getMonths()->获取相差的月 getDays()->获取相差的天
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private static void period () { LocalDate local1 = LocalDate.of(2022 , 12 , 12 ); LocalDate local2 = LocalDate.of(2021 , 11 , 11 ); Period period = Period.between(local2, local1); System.out.println(period.getYears()); System.out.println(period.getMonths()); System.out.println(period.getDays()); }
Duration计算时间之间的偏差 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1. static Duration between (Temporal startInclusive, Temporal endExclusive) -> 计算时间差2. Temporal : 是一个接口 实现类:LocalDate LocalDateTime 3. 参数需要传递 Temporal 的实现类对象, 注意要传递LocalDateTime 因为Duration计算精确时间偏差,所以需要传递能操作精确时间的 LocalDateTime 4. 利用Dutation获取相差的时分秒 -> to开头 toDays() :获取相差天数 toHours(): 获取相差小时 toMinutes():获取相差分钟 toMillis():获取相差秒(毫秒)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 private static void duration () { LocalDateTime local1 = LocalDateTime.of(2022 , 12 , 12 ,12 ,12 ,12 ); LocalDateTime local2 = LocalDateTime.of(2021 , 11 , 11 ,11 ,11 ,11 ); Duration duration = Duration.between(local2, local1); System.out.println(duration.toDays()); System.out.println(duration.toHours()); System.out.println(duration.toMinutes()); System.out.println(duration.toMillis()); }
如果计算年月日 ,就用Period
如果计算时分秒,就用Duration
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. 获取: static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern (String pattern) -> 获取对象,指定格式 2. 方法: String format (TemporalAccessor temporal) -> 将日期对象按照指定的规则转成String TemporalAccessor:接口,子接口有Temporal Temporal的实现类:LocalDate LocalDateTime TemporalAccessor parse (CharSequence text) -> 将符合规则的字符串转成日期对象 如果想将TemporalAccessor转成我们常见的LocalDateTime日期对象,就需要用到LocalDateTime中的静态方法: static LocalDateTime from (TemporalAccessor temporal)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private static void parse () { DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ); String time = "2000-10-10 10:10:10" ; TemporalAccessor temporalAccessor = dtf.parse(time); LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.from(temporalAccessor); System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime); String formatTime = dtf.format(localDateTime); System.out.println("formatTime = " + formatTime); }
System类 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. 概述:系统相关类,是一个工具类2. 特点: a.构造私有,不能利用构造方法new 对象 b.方法都是静态的 3. 使用: 类名直接调用
方法
说明
static long currentTimeMillis()
返回以毫秒为单位的当前时间,可以测效率
static void exit(int status)
终止当前正在运行的 Java 虚拟机
static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length
数组复制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class Demo01System { public static void main (String[] args) { arraycopy(); } private static void arraycopy () { int [] arr1 = {1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 }; int [] arr2 = new int [10 ]; System.arraycopy(arr1,0 ,arr2,0 ,5 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < arr2.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr2[i]+" " ); } } private static void exit () { for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { if (i==5 ){ System.exit(0 ); } System.out.println("helloworld" +i); } } private static void currentTimeMillis () { long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("time = " + time); } }
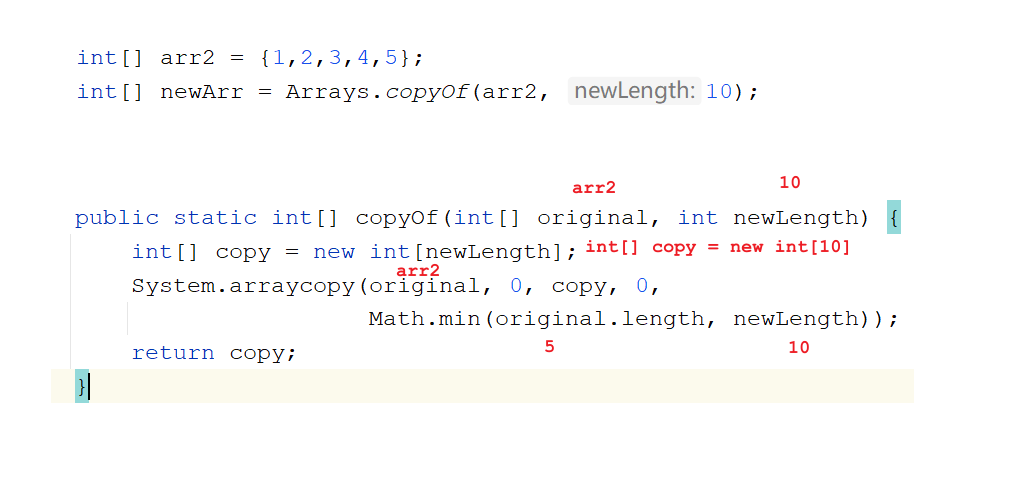
Arrays数组工具类 1 2 3 4 5 1. 概述:数组工具类2. 特点: a.构造私有 b.方法静态 3. 使用:类名直接调用
方法
说明
static String toString(int[] a)
按照格式打印数组元素
static void sort(int[] a)
升序排序
static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key)
二分查找(前提是升序)
static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength)
数组扩容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.util.Arrays;public class Demo02Arrays { public static void main (String[] args) { int [] arr = {5 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 5 , 4 , 7 }; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); System.out.println("==============" ); Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); System.out.println("==============" ); int [] arr1 = {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 }; int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr1, 3 ); System.out.println("index = " + index); System.out.println("==============" ); int [] arr2 = {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 }; int [] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr2, 10 ); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr)); arr2 = newArr; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2)); } }
包装类 基本数据类型对应的引用数据类型(包装类) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 概述:就是基本类型对应的类(包装类),我们需要将基本类型转成包装类,从而让基本类型拥有类的特性(说白了,将基本类型转成包装类之后,就可以使用包装类中的方法操作数据) 2. 为啥要学包装类: a.将来有一些特定场景,特定操作,比如调用方法传递包装类 比如:ArrayList集合,里面有一个方法add(Integer i),此时我们不能调用add方法之后直接传递基本类型,因为引用类型不能直接接收基本类型的值,就需要先将基本类型转成包装类,传递到add方法中 b.将来我们还可以将包装类转成基本类型: 包装类不能直接使用+ - * /,所以需要将包装类转成基本类型,才能使用+ - * /
基本类型
包装类
byte
Byte
short
Short
int
Integer
long
Long
float
Float
double
Double
char
Charactor
boolean
Boolean
Integer的介绍以及使用 Integer基本使用 1 2 3 4 1. 概述:Integer是int 的包装类2. 构造: 不推荐使用了,但是jkd1.8 还能用,jdk17已不能使用 Integer(int value) Integer(String s) s必须是数字形式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Demo01Integer { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer i1 = new Integer (10 ); System.out.println("i1 = " + i1); Integer i2 = new Integer ("10" ); System.out.println("i2 = " + i2); System.out.println("================" ); Boolean b1 = new Boolean ("true" ); System.out.println("b1 = " + b1); Boolean b2 = new Boolean ("false" ); System.out.println("b2 = " + b2); Boolean b3 = new Boolean ("True" ); System.out.println("b3 = " + b3); } }
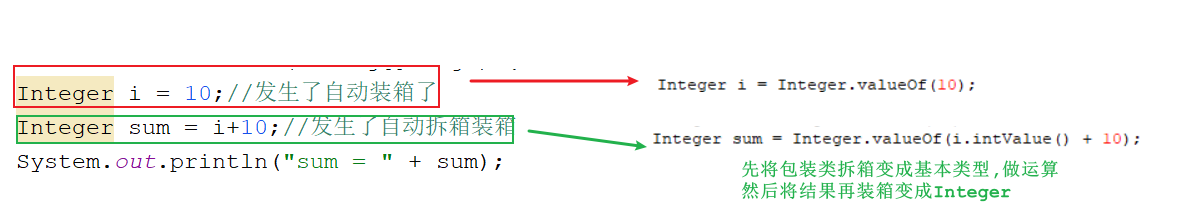
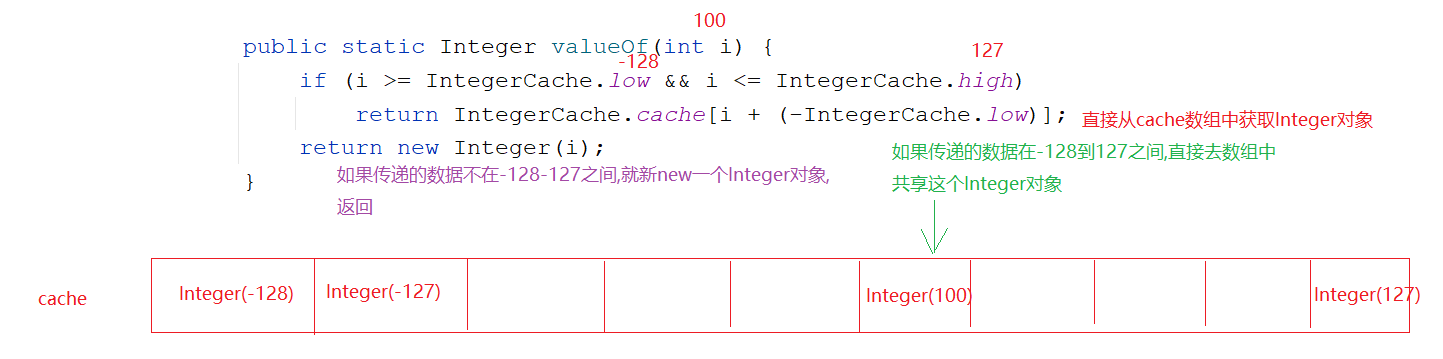
1 2 3 4 1. 装箱:将基本类型转成对应的包装类2. 方法: static Integer valueOf (int i) static Integer valueOf (String s)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Demo02Integer { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10 ); System.out.println("i1 = " + i1); Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf("100" ); System.out.println("i2 = " + i2); } }
1 2 3 1. 拆箱:将包装类转成基本类型2. 方法: int intValue () ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Demo03Integer { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10 ); System.out.println("i1 = " + i1); int i = i1.intValue(); System.out.println("(i+10) = " + (i + 10 )); } }
自动拆箱装箱 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class Demo04Integer { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer i = 10 ; Integer sum = i+10 ; System.out.println("sum = " + sum); } }
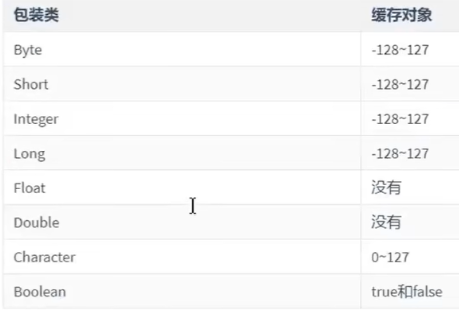
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Demo05Integer { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer i1 = 100 ; Integer i2 = 100 ; System.out.println(i1 == i2); Integer i3 = 128 ; Integer i4 = 128 ; System.out.println(i3 == i4); } }
基本类型和String之间的转换 基本类型往String转 1 2 3 4 1. 方式1 : + 拼接 2. 方式2 :String中的静态方法 static String valueOf (int i)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private static void method01 () { int i = 10 ; String s1 = i+"" ; System.out.println(s1+1 ); System.out.println("============" ); String s = String.valueOf(10 ); System.out.println(s+1 ); }
String转成基本数据类型 1 每个包装类中都有一个类似的方法: parseXXX
位置
方法
说明
Byte
static byte parseByte(String s)
将String转byte类型
Short
static short parseShort(String s)
将String转成short类型
Integer
static int parseInt(String s)
将String转成int类型
Long
static long parseLong(String s)
将String转成long类型
Float
static float parseFloat(String s)
将String转成float类型
Double
static double parseDouble(String s)
将String转成double类型
Boolean
static boolean parseBoolean(String s)
将String转成boolean类型
1 2 3 4 private static void method02 () { int number = Integer.parseInt("1111" ); System.out.println(number+1 ); }
如何定义一个标准javabean
在 Java 中,一个标准的 JavaBean 是一个遵循特定命名和设计约定的类。JavaBean 通常用于封装数据,并且可以通过反射机制进行访问和操作。以下是定义一个标准 JavaBean 的主要规范:
1. 私有属性(Private Fields) JavaBean 的属性通常是私有的(private),这意味着它们不能直接从类的外部访问。
2. 公共的 getter 和 setter 方法 为了访问和修改私有属性,JavaBean 提供了公共的 getter 和 setter 方法。这些方法的命名遵循特定的约定:
Getter 方法 :用于获取属性的值。如果属性名为 propertyName,则 getter 方法通常命名为 getPropertyName()。如果属性是布尔类型,getter 方法可以命名为 isPropertyName()。Setter 方法 :用于设置属性的值。如果属性名为 propertyName,则 setter 方法通常命名为 setPropertyName(Type value)。
3. 无参构造方法 JavaBean 必须提供一个无参的公共构造方法(默认构造方法),以便可以通过反射机制实例化对象。
4. 实现 Serializable 接口(可选) 为了支持序列化和反序列化,JavaBean 可以实现 java.io.Serializable 接口。
关键点总结
私有属性 :属性通常是私有的,以封装数据。Getter 和 Setter 方法 :提供公共的 getter 和 setter 方法来访问和修改私有属性。无参构造方法 :提供一个无参的公共构造方法,以便可以通过反射机制实例化对象。实现 Serializable 接口 (可选):为了支持序列化和反序列化,可以实现 Serializable 接口。
定义javabean的时候一般会将基本类型的属性定义成包装类型的属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1.举例:如果uid为Integer型,默认值是null 2.将来javabean中的数据都是和数据库表联系起来的,我们可以将javabean中的数据添加到表中 如果表中的uid为主键自增的,此时添加语句时uid中的数据不用我们单独维护赋值了,添加语句的sql语句就可以这样写: insert into user(uid,username,password) values (NULL,'金莲','36666'); 3.到时候,我们需要将javabean中封装的数据获取出来放到sql语句中,如果uid为主键自增,而且javabean中的uid为包装类型,默认值为NULL,这样就不用单独维护uid的值了,也不用先给javabean中的uid赋值,然后在保存到数据库中了,咱们就可以直接使用uid的默认值,将默认值放到sql语句的uid列中 4.而且将javabean中的属性变成包装类,还可以使用包装类中的方法去操作此属性值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class User { private Integer uid; private String username; private String password; public User () { } public User (Integer uid, String username, String password) { this .uid = uid; this .username = username; this .password = password; } public Integer getUid () { return uid; } public void setUid (Integer uid) { this .uid = uid; } public String getUsername () { return username; } public void setUsername (String username) { this .username = username; } public String getPassword () { return password; } public void setPassword (String password) { this .password = password; } }
总结 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 模块15回顾: 1.Math:数学工具类 abs ceil floor round max min 2.BigInteger:处理超大整数 a.构造:BigInteger(String s) b.方法: add subtract multiply divide 3.BigDecimal:处理小数直接做运算而产生的精度损失问题 a.构造:BigDecimal(String s) b.方法: add subtract multiply divide valueOf(double b) divide(BigDecimal b,保留几位小数,取舍方式) 4.Date:日期类 a.构造: Date() Date(long time) b.方法: long getTime()获取时间对应的毫秒值 void setTime(long time) 设置时间,从时间原点开始算 5.Calendar:日历类 a.获取:getInstance() b.方法: get(指定的时间字段) set (指定字段,值) add(指定的时间字段,值) -> 设置时间偏移量 getTime()将Calendar转成Date 6.SimpleDateFormat:日期格式化类 a.构造:SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) b.方法: format parse 7.jdk8新日期类: a.LocalDate:操作年月日 now of b.LocalDateTime:操作年月日时分秒 now of c.获取字段:get开头 d.设置字段:with开头 e.时间偏移 plus开头 -> 向后偏移 minus开头 -> 向前偏题 f.计算时间偏差: Period Duration between方法 g.DateTimeFormatter:日期格式化类 获取:ofPattern() 方法: format parse 8.System类: arrayCopy(源数组,第源数组第几个索引开始复制,目标数组,从目标数组第几个索引开始粘贴,粘贴多少个) 9.Arrays数组工具类: toString(数组)按照格式打印数组 binarySearch(数组,要查找的元素) -> 二分查找 sort (数组)升序排序 copyOf(数组,指定新数组长度) -> 数组扩容 10.包装类:基本类型对应的包装类 byte Byte short Short int Integer long Long float Float double Double char Charactor boolean Boolean 11.Integer: a.构造: Integer(int i) Integer(String s) b.装箱: valueOf(int i) valueOf(String s) c.拆箱: intValue() 12.基本类型和String之间的转换 a.基本转String +"" valueOf() b.String转基本 包装类中的parsexxx() 13.javabean:定义的时候基本类型的属性要改成包装类