在线视频:尚硅谷2024最新Java入门视频教程(下部)-集合 尚硅谷2024新版Java基础 https://gitee.com/an_shiguang/learn-java
重点内容:
1.知道集合的特点以及作用
集合框架(单列集合) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1. 之前我们学了保存数据的有:变量,数组,但是数组定长,所以如果添加一个数据或者删除一个数据,数组并不好使,需要创建新数组,所以接下来我们学一个长度可变的容器,集合 2. 集合的特点 a.只能存储引用数据类型的数据 b.长度可变 c.集合中有大量的方法,方便我们操作 3. 分类: a.单列集合:一个元素就一个组成部分: list.add("张三" ) b.双列集合:一个元素有两部分构成: key 和 value map.put("涛哥" ,"金莲" ) -> key,value叫做键值对
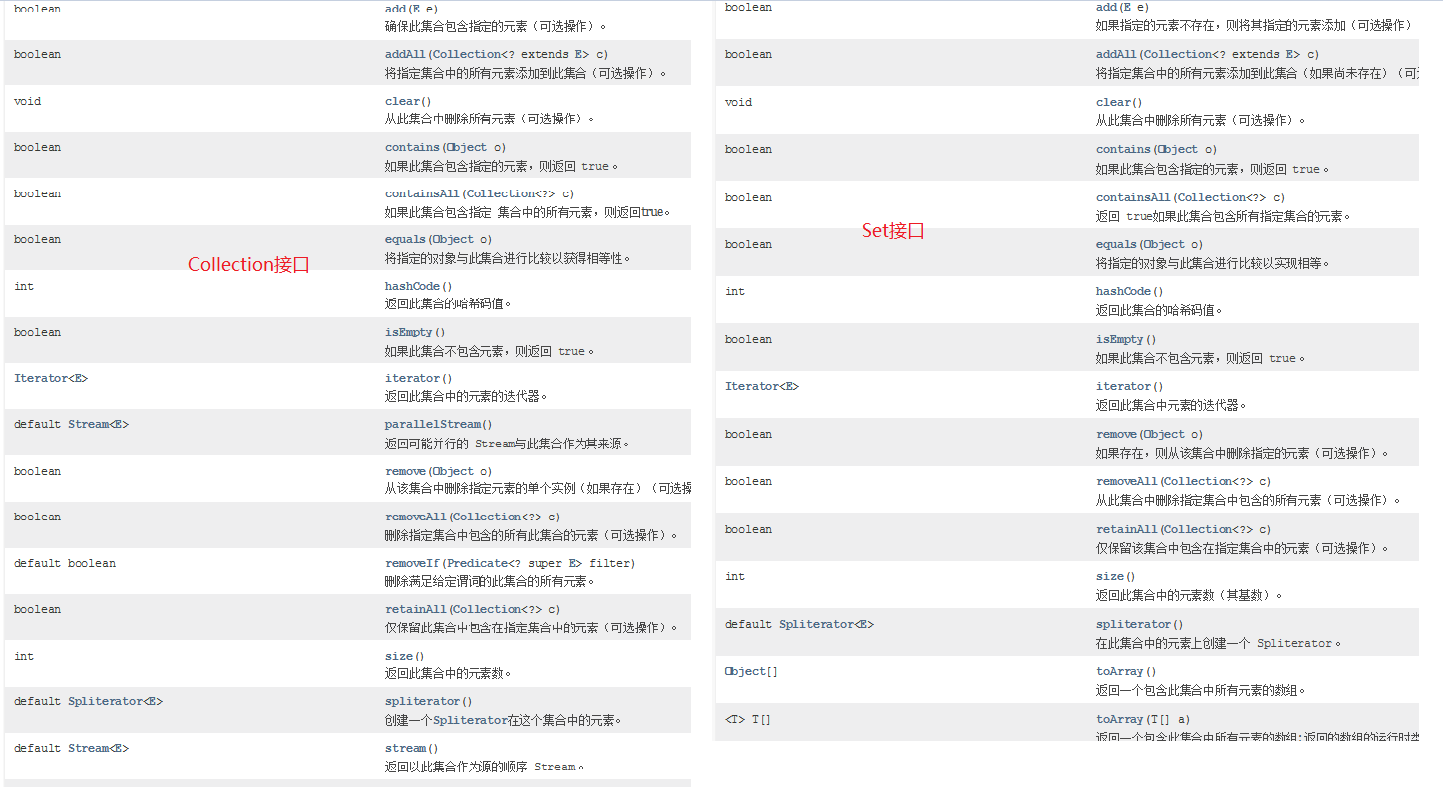
Collection接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 1. 概述:单列集合的顶级接口2. 使用: a.创建: Collection<E> 对象名 = new 实现类对象<E>() b.<E>:泛型,决定了集合中能存储什么类型的数据,可以统一元素类型 泛型中只能写引用数据类型,如果不写,默认Object类型,此时什么类型的数据都可以存储了 <int > 不行 <Integer> 行 <Person> 行 c.泛型细节: 我们等号前面的泛型必须写,等号后面的泛型可以不写,jvm会根据前面的泛型推导出后面的泛型是啥 3. 常用方法: boolean add (E e) : 将给定的元素添加到当前集合中(我们一般调add时,不用boolean 接收,因为add一定会成功) boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) :将另一个集合元素添加到当前集合中 (集合合并) void clear () :清除集合中所有的元素 boolean contains (Object o) :判断当前集合中是否包含指定的元素 boolean isEmpty () : 判断当前集合中是否有元素->判断集合是否为空 boolean remove (Object o) :将指定的元素从集合中删除 int size () :返回集合中的元素个数。 Object[] toArray(): 把集合中的元素,存储到数组中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class Demo01Collection { public static void main (String[] args) { Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList <>(); collection.add("萧炎" ); collection.add("萧薰儿" ); collection.add("彩鳞" ); collection.add("小医仙" ); collection.add("云韵" ); collection.add("涛哥" ); System.out.println(collection); Collection<String> collection1 = new ArrayList <>(); collection1.add("张无忌" ); collection1.add("小昭" ); collection1.add("赵敏" ); collection1.add("周芷若" ); collection1.addAll(collection); System.out.println(collection1); collection1.clear(); System.out.println(collection1); boolean result01 = collection.contains("涛哥" ); System.out.println("result01 = " + result01); System.out.println(collection1.isEmpty()); collection.remove("涛哥" ); System.out.println(collection); System.out.println(collection.size()); Object[] arr = collection.toArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } }
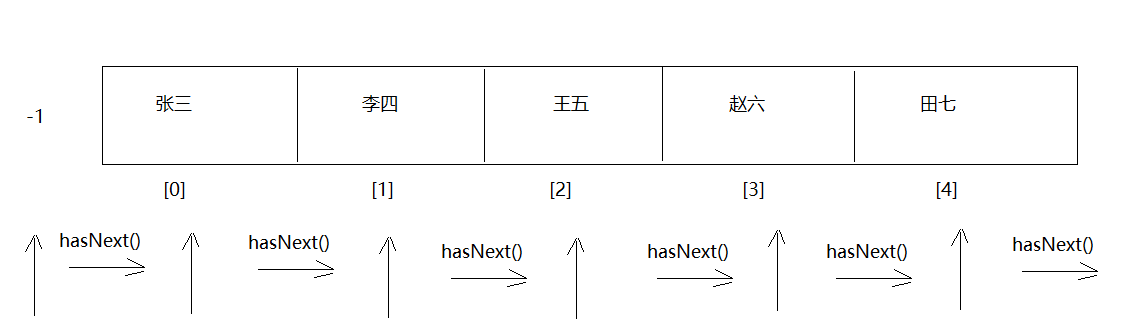
迭代器 迭代器基本使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 概述:Iterator接口2. 主要作用:遍历集合3. 获取:Collection中的方法: Iterator<E> iterator () 4. 方法: boolean hasNext () -> 判断集合中有没有下一个元素 E next () ->获取下一个元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Demo01Iterator { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("楚雨荨" ); list.add("慕容云海" ); list.add("端木磊" ); list.add("上官瑞谦" ); list.add("叶烁" ); Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String element = iterator.next(); System.out.println(element); } } }
注意:next方法在获取的时候不要连续使用多次,否则可能会出现NoSuchElementException
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Demo02Iterator { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("楚雨荨" ); list.add("慕容云海" ); list.add("端木磊" ); list.add("上官瑞谦" ); list.add("叶烁" ); Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { String element = iterator.next(); System.out.println(element); } } }
迭代器迭代过程 1 2 3 4 5 6 int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ;public boolean hasNext () { return cursor !=size }
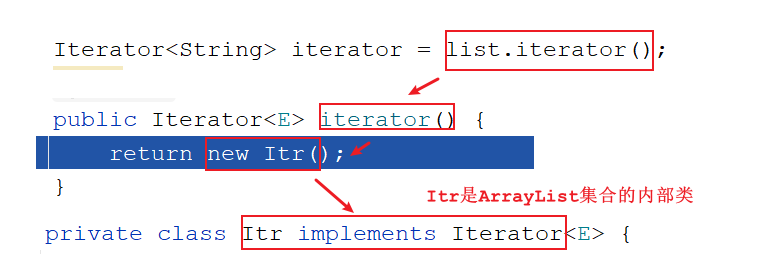
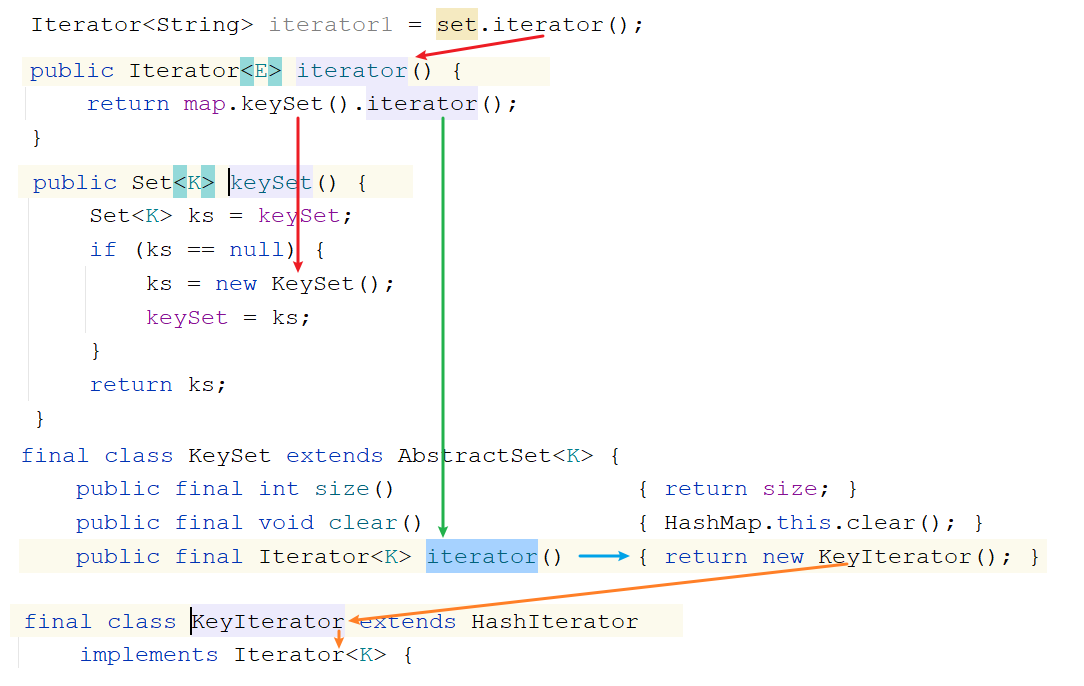
迭代器底层原理 1 2 3 4 1. 获取Iterator的时候怎么获取的: Iterator iterator = list.iterator() 我们知道Iterator是一个接口,等号右边一定是它的实现类对象 问题:Iterator接收的到底是哪个实现类对象呢? -> ArrayList中的内部类Itr对象
注意:只有ArrayList使用迭代器的时候Iterator接口才会指向Itr,其他的集合使用迭代器Iterator就指向的不是Itr了
1 2 HashSet<String> set = new HashSet <>(); Iterator<String> iterator1 = set.iterator();
并发修改异常 1 需求:定义一个集合,存储 唐僧,孙悟空,猪八戒,沙僧,遍历集合,如果遍历到猪八戒,往集合中添加一个白龙马
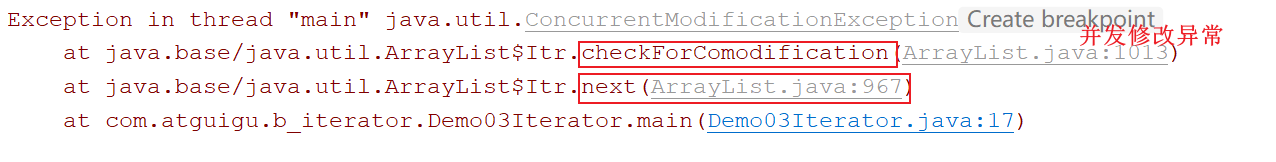
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Demo03Iterator { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("唐僧" ); list.add("孙悟空" ); list.add("猪八戒" ); list.add("沙僧" ); Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String element = iterator.next(); if ("猪八戒" .equals(element)){ list.add("白龙马" ); } } System.out.println(list); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 String element = iterator.next();========================================= private class Itr implements Iterator <E> { int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = modCount; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next () { checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } }
1 结论:当预期操作次数和实际操作次数不相等了,会出现"并发修改异常"
1 我们干了什么事儿,让实际操作次数和预期操作次数不相等了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 list.add("白龙马" ) ==================================== public boolean add (E e) { modCount++; } ==================================== 最终结论:我们调用了add方法,而add方法底层只给modCount++,但是再次调用next方法的时候,并没有给修改后的modCount重新赋值给expectedModCount,导致next方法底层的判断判断出实际操作次数和预期操作次数不相等了,所以抛出了"并发修改异常"
ArrayList中的方法:ListIterator listIterator()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Demo03Iterator { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("唐僧" ); list.add("孙悟空" ); list.add("猪八戒" ); list.add("沙僧" ); ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator(); while (listIterator.hasNext()){ String element = listIterator.next(); if ("猪八戒" .equals(element)){ listIterator.add("白龙马" ); } } System.out.println(list); } }
使用迭代器迭代集合的过程中,不要随意修改集合长度,容易出现并发修改异常
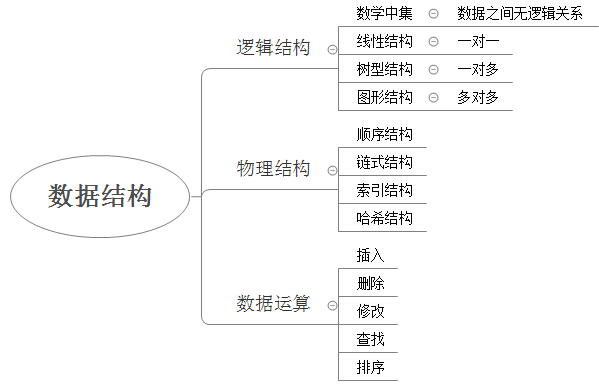
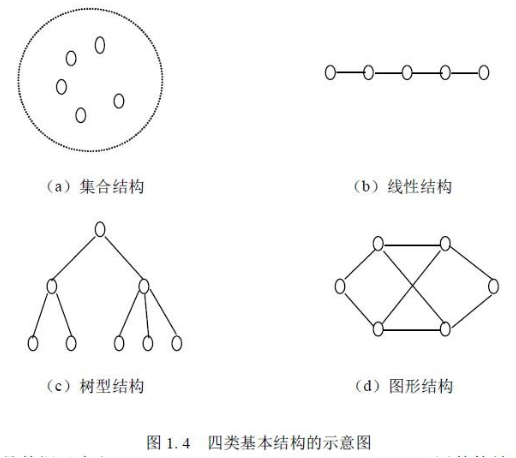
数据结构 1 数据结构是一种具有一定逻辑关系,在计算机中应用某种存储结构,并且封装了相应操作的数据元素集合。它包含三方面的内容,逻辑关系、存储关系及操作。
为什么需要数据结构 1 随着应用程序变得越来越复杂和数据越来越丰富,几百万、几十亿甚至几百亿的数据就会出现,而对这么大对数据进行搜索、插入或者排序等的操作就越来越慢,数据结构就是用来解 决这些问题的。
数据的逻辑结构指反映数据元素之间的逻辑关系,而与他们在计算机中的存储位置无关:
集合(数学中集合的概念):数据结构中的元素之间除了“同属一个集合” 的相互关系外,别无其他关系;
线性结构:数据结构中的元素存在一对一的相互关系;
树形结构:数据结构中的元素存在一对多的相互关系;
图形结构:数据结构中的元素存在多对多的相互关系。
数据的物理结构/存储结构:是描述数据具体在内存中的存储(如:顺序结构、链式结构、索引结构、哈希结构)等,一种数据逻辑结构可表示成一种或多种物理存储结构。
数据结构是一门完整并且复杂的课程,那么我们今天只是简单的讨论常见的几种数据结构,让我们对数据结构与算法有一个初步的了解。
栈
队列
数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 特点:查询快,增删慢2. 查询快:因为有索引,我们可以直接通过索引操作元素 增删慢:因为数组定长 a.添加元素:创建新数组,将老数组中的元素复制到新数组中去,在最后添加新元素;要是从中间插入就更麻烦了 插入完新元素,后面的元素都要往后移动 b.删除元素:创建新数组,将老数组中的元素复制到新数组中去,被删除的元素就不复制了;如果要是从之间删除 被删除的元素后面的元素都要往前移动
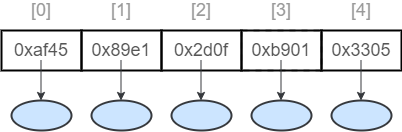
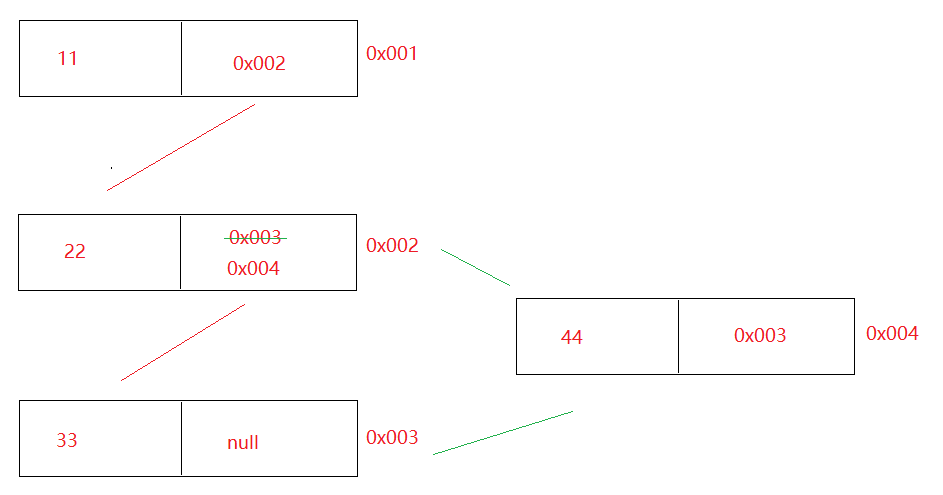
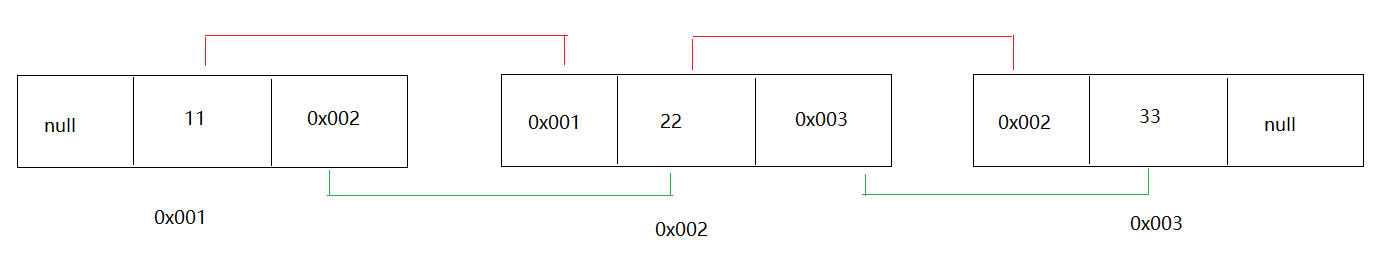
链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1. 在集合中涉及到了两种链表2. 单向链表 a.节点:一个节点分为两部分 第一部分:数据域(存数据) 第二部分:指针域(保存下一个节点地址) b.特点:前面节点记录后面节点的地址,但是后面节点地址不记录前面节点地址 3. 双向链表: a.节点:一个节点分为三部分 第一部分:指针域(保存上一个节点地址) 第二部分:数据域(保存的数据) 第三部分:指针域(保存下一个节点地址) b.特点: 前面节点记录后面节点地址,后面节点也记录前面节点地址 4. 链表结构特点:查询慢,增删快
单向链表 1 2 3 4 a.节点:一个节点分为两部分 第一部分:数据域(存数据) 第二部分:指针域(保存下一个节点地址) b.特点:前面节点记录后面节点的地址,但是后面节点地址不记录前面节点地址
双向链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 a.节点:一个节点分为三部分 第一部分:指针域(保存上一个节点地址) 第二部分:数据域(保存的数据) 第三部分:指针域(保存下一个节点地址) b.特点: 前面节点记录后面节点地址,后面节点也记录前面节点地址
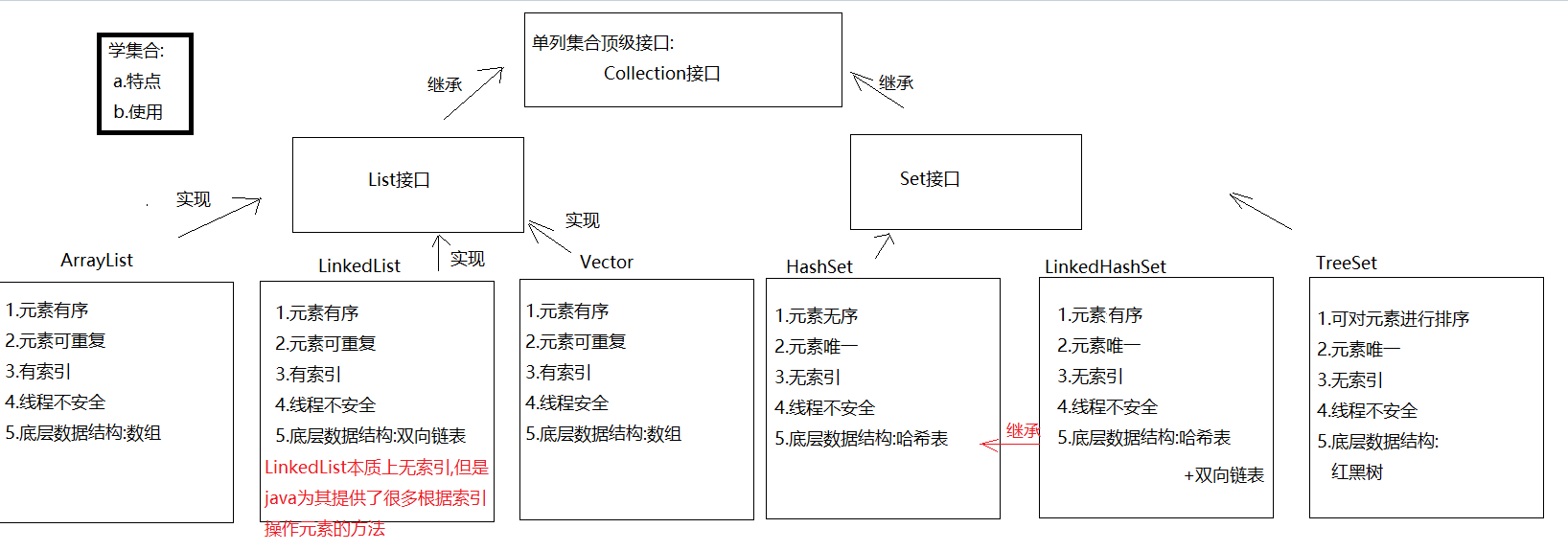
List接口 1 2 3 1. 概述:是Collection接口的子接口2. 常见的实现类: ArrayList LinkedList Vector
List集合下的实现类 ArrayList集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1. 概述:ArrayList是List接口的实现类2. 特点: a.元素有序-> 按照什么顺序存的,就按照什么顺序取 b.元素可重复 c.有索引-> 可以利用索引去操作元素 d.线程不安全 3. 数据结构:数组 4. 常用方法: boolean add (E e) -> 将元素添加到集合中->尾部(add方法一定能添加成功的,所以我们不用boolean 接收返回值) void add (int index, E element) ->在指定索引位置上添加元素 boolean remove (Object o) ->删除指定的元素,删除成功为true ,失败为false E remove (int index) -> 删除指定索引位置上的元素,返回的是被删除的那个元素 E set (int index, E element) -> 将指定索引位置上的元素,修改成后面的element元素 E get (int index) -> 根据索引获取元素 int size () -> 获取集合元素个数
ArrayList集合使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Demo01ArrayList { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("铁胆火车侠" ); list.add("喜洋洋" ); list.add("火影忍者" ); list.add("灌篮高手" ); list.add("网球王子" ); System.out.println(list); list.add(2 ,"涛哥" ); System.out.println(list); list.remove("涛哥" ); System.out.println(list); String element = list.remove(0 ); System.out.println(element); System.out.println(list); String element2 = list.set(0 , "金莲" ); System.out.println(element2); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list.get(0 )); System.out.println(list.size()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Demo02ArrayList { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("铁胆火车侠" ); list.add("喜洋洋" ); list.add("火影忍者" ); list.add("灌篮高手" ); list.add("网球王子" ); Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("=====================" ); for (int i = 0 ;i<list.size();i++){ System.out.println(list.get(i)); } System.out.println("=====================" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class Demo03ArrayList { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(2 ); System.out.println(list); list.remove(Integer.valueOf(2 )); System.out.println(list); } }
底层源码分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. ArrayList构造方法: a.ArrayList() 构造一个初始容量为十的空列表 b.ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 构造具有指定初始容量的空列表 2. ArrayList源码总结: a.不是一new 底层就会创建初始容量为10 的空列表,而是第一次add的时候才会创建初始化容量为10 的空列表 b.ArrayList底层是数组,那么为啥还说集合长度可变呢? ArrayList底层会自动扩容-> Arrays.copyOf c.扩容多少倍? 1.5 倍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 ArrayList() 构造一个初始容量为十的空列表 ========================================= private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};Object[] elementData; ->ArrayList底层的那个数组 public ArrayList () { this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } ========================================= list.add("a" ); public boolean add (E e) { modCount++; add(e, elementData, size); return true ; } private void add (E e->元素, Object[] elementData->集合数组, int s->0 ) { if (s == elementData.length) elementData = grow(); elementData[s] = e; size = s + 1 ; } private Object[] grow() { return grow(size + 1 ); } private Object[] grow(int minCapacity->1 ) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity, minCapacity - oldCapacity, oldCapacity >> 1 ); return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } else { return elementData = new Object [Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY->10 , minCapacity->1 )]; } } ========================================== 假设ArrayList中存了第11 个元素,会自动扩容-> Arrays.copyOf private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { int newCapacity (15 ) = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity->10 , minCapacity - oldCapacity->1 , oldCapacity >> 1 ->5 ); return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } else { return elementData = new Object [Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)]; } } public static int newLength (int oldLength->10 , int minGrowth->1 , int prefGrowth->5 ) { int prefLength = oldLength + Math.max(minGrowth, prefGrowth); if (0 < prefLength && prefLength <= SOFT_MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH) { return prefLength; } else { return hugeLength(oldLength, minGrowth); } }
1 ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 构造具有指定初始容量的空列表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(5 ); ============================================== public ArrayList (int initialCapacity->5 ) { if (initialCapacity > 0 ) { this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); } }
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>() -> 现在我们想用都是new
但是将来开发不会想使用就new集合,都是调用一个方法,查询出很多数据来,此方法返回一个集合,自动将查询出来的数据放到集合中,我们想在页面上展示数据,遍历集合
而且将来调用方法,返回的集合类型,一般都是接口类型
List<泛型> list = 对象.查询方法()
LinkedList集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1. 概述:LinkedList是List接口的实现类2. 特点: a.元素有序 b.元素可重复 c.有索引 -> 这里说的有索引仅仅指的是有操作索引的方法,不代表本质上具有索引 d.线程不安全 3. 数据结构:双向链表 4. 方法:有大量直接操作首尾元素的方法 - public void addFirst (E e) :将指定元素插入此列表的开头。 - public void addLast (E e) :将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。 - public E getFirst () :返回此列表的第一个元素。 - public E getLast () :返回此列表的最后一个元素。 - public E removeFirst () :移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。 - public E removeLast () :移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。 - public E pop () :从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。 - public void push (E e) :将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。 - public boolean isEmpty () :如果列表没有元素,则返回true 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class Demo05LinkedList { public static void main (String[] args) { LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList <>(); linkedList.add("吕布" ); linkedList.add("刘备" ); linkedList.add("关羽" ); linkedList.add("张飞" ); linkedList.add("貂蝉" ); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.addFirst("孙尚香" ); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.addLast("董卓" ); System.out.println(linkedList); System.out.println(linkedList.getFirst()); System.out.println(linkedList.getLast()); linkedList.removeFirst(); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeLast(); System.out.println(linkedList); System.out.println("======================" ); Iterator<String> iterator = linkedList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("=======================" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < linkedList.size(); i++) { System.out.println(linkedList.get(i)); } } }
1 2 public E pop () :从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。public void push (E e) :将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo06LinkedList { public static void main (String[] args) { LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList <>(); linkedList.add("吕布" ); linkedList.add("刘备" ); linkedList.add("关羽" ); linkedList.add("张飞" ); linkedList.add("貂蝉" ); linkedList.pop(); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.push("涛哥" ); System.out.println(linkedList); } }
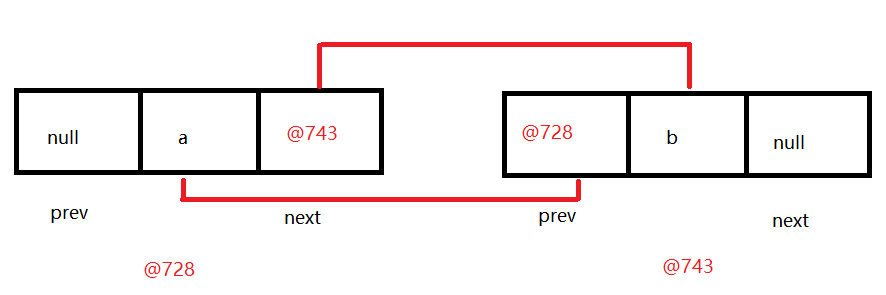
LinkedList底层成员解释说明 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1. LinkedList底层成员 transient int size = 0 ; 元素个数 transient Node<E> first; 第一个节点对象 transient Node<E> last; 最后一个节点对象 2. Node代表的是节点对象 private static class Node <E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this .item = element; this .next = next; this .prev = prev; } }
LinkedList中add方法源码分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList <>(); list.add("a" ); list.add("b" ); void linkLast (E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node <>(l, e, null ); last = newNode; if (l == null ) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
LinkedList中get方法源码分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public E get (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } Node<E> node (int index) { if (index < (size >> 1 )) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1 ; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
1 index < (size >> 1 )采用二分思想,先将index与长度size的一半比较,如果index<size/2 ,就只从位置0 往后遍历到位置index处,而如果index>size/2 ,就只从位置size往前遍历到位置index处。这样可以减少一部分不必要的遍历
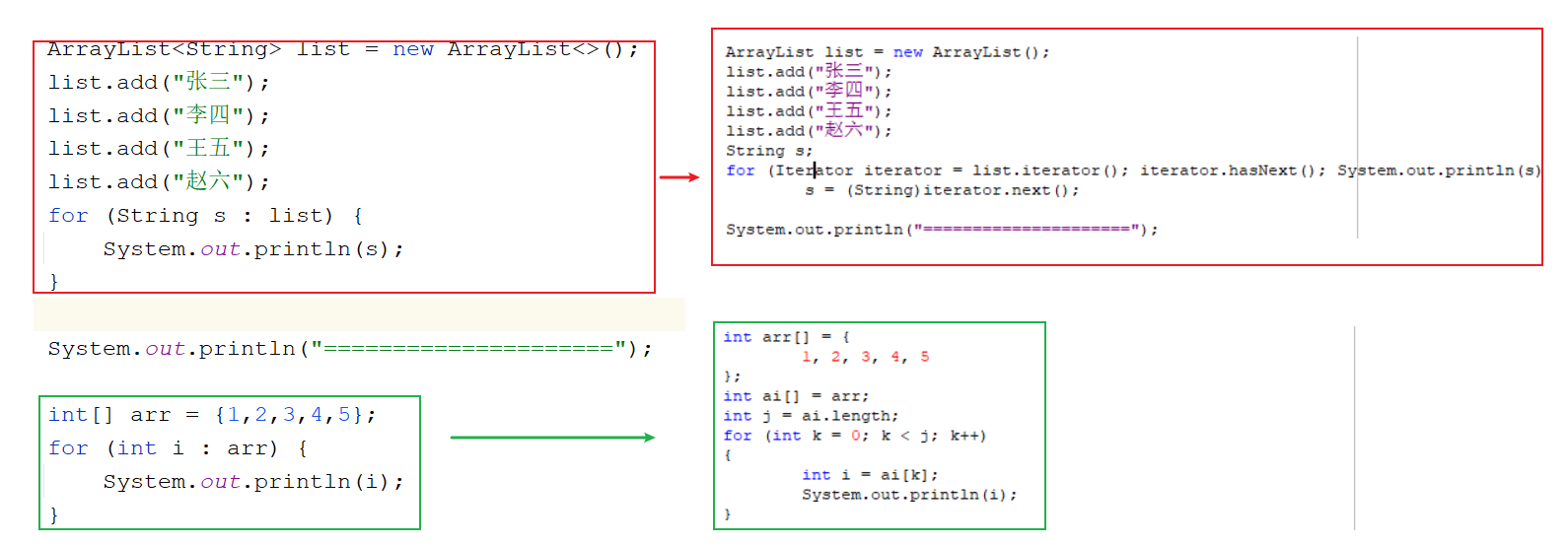
增强for 基本使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. 作用: 遍历集合或者数组 2. 格式: for (元素类型 变量名:要遍历的集合名或者数组名){ 变量名就是代表的每一个元素 } 3. 快捷键:集合名或者数组名.for
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Demo01ForEach { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("张三" ); list.add("李四" ); list.add("王五" ); list.add("赵六" ); for (String s : list) { System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("=====================" ); int [] arr = {1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 }; for (int i : arr) { System.out.println(i); } } }
注意 1 2 1. 增强for 遍历集合时,底层实现原理为迭代器2. 增强for 遍历数组时,底层实现原理为普通for
所以不管是用迭代器还是使用增强for,在遍历集合的过程中都不要随意修改集合长度,否则会出现并发修改异常
模块十八总结及模块十九重点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 模块18回顾: 1.Collection集合:单列集合的顶级接口 a.add addAll clear size isEmpty remove toArray contains 2.迭代器:Iterator a.获取:iterator方法 b.方法: hasNext() next() c.并发修改异常:在迭代集合的时候,不能随意修改集合长度 原因:调用add,只给实际操作次数+1.后面调用next的时候,没有给预期操作次数重新赋值,导致预期操作次数和实际操作次数不相等了 3.数据结构: 栈:先进后出 队列:先进先出 数组:查询快,增删慢 链表:查询慢,增删快 4.ArrayList a.特点: 元素有序,有索引,元素可重复,线程不安全 b.数据结构: 数组 c.方法: add(元素)直接在最后添加元素 add(索引,元素)在指定索引位置上添加元素 remove(元素)删除指定元素 remove(索引)按照指定索引删除元素 size()获取元素个数 get(索引)根据索引获取元素 set(索引,元素)将指定索引位置上的元素修改成我们指定的元素 d.利用无参构造创建集合对象,第一次add时,会创建一个长度为10的空数组 超出范围,自动扩容->Arrays.copyOf 扩容1.5倍 5.LinkedList a.特点: 元素有序 有索引(java提供了按照索引操作元素的方法,并不代表本质上拥有索引),元素可重复,线程不安全 b.数据结构:双向链表 c.方法:有大量直接操作收尾元素的方法 6.增强for: a.格式: for(元素类型 变量名:集合名或者数组名){ 变量就代表每一个元素 } b.原理: 遍历集合时,原理为迭代器 遍历数组时,原理为普通for 模块19重点: 1.会Collections集合工具类的常用方法 2.会使用泛型 3.知道HashSet和LinkedHashSet的特点以及使用 4.知道HashSet将元素去重复的过程
Collections集合工具类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. 概述:集合工具类2. 特点: a.构造私有 b.方法都是静态的 3. 使用:类名直接调用 4. 方法: static <T> boolean addAll (Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) ->批量添加元素 static void shuffle (List<?> list) ->将集合中的元素顺序打乱 static <T> void sort (List<T> list) ->将集合中的元素按照默认规则排序 static <T> void sort (List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) ->将集合中的元素按照指定规则排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class Demo01Collections { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); Collections.addAll(list,"张三" ,"李四" ,"王五" ,"赵六" ,"田七" ,"朱八" ); System.out.println(list); Collections.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list); ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); list1.add("c.举头望明月" ); list1.add("a.床前明月光" ); list1.add("d.低头思故乡" ); list1.add("b.疑是地上霜" ); Collections.sort(list1); System.out.println(list1); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 方法:static <T> void sort (List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) ->将集合中的元素按照指定规则排序 2. Comparator比较器 a.方法: int compare (T o1,T o2) o1-o2 -> 升序 o2-o1 -> 降序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo02Collections { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(new Person ("柳岩" ,18 )); list.add(new Person ("涛哥" ,16 )); list.add(new Person ("金莲" ,20 )); Collections.sort(list, new Comparator <Person>() { @Override public int compare (Person o1, Person o2) { return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge(); } }); System.out.println(list); } }
1 2 1. 接口:Comparable接口2. 方法: int compareTo (T o) -> this -o (升序) o-this (降序)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class Student implements Comparable <Student>{ private String name; private Integer score; public Student () { } public Student (String name, Integer score) { this .name = name; this .score = score; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getScore () { return score; } public void setScore (Integer score) { this .score = score; } @Override public String toString () { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", score=" + score + '}' ; } @Override public int compareTo (Student o) { return this .getScore()-o.getScore(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo03Collections { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(new Student ("涛哥" ,100 )); list.add(new Student ("柳岩" ,150 )); list.add(new Student ("三上" ,80 )); Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list); } }
1 2 Arrays中的静态方法: static <T> List<T> asList(T...a) -> 直接指定元素,转存到list集合中
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Demo04Collections { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = Arrays.asList("张三" , "李四" , "王五" ); System.out.println(list); } }
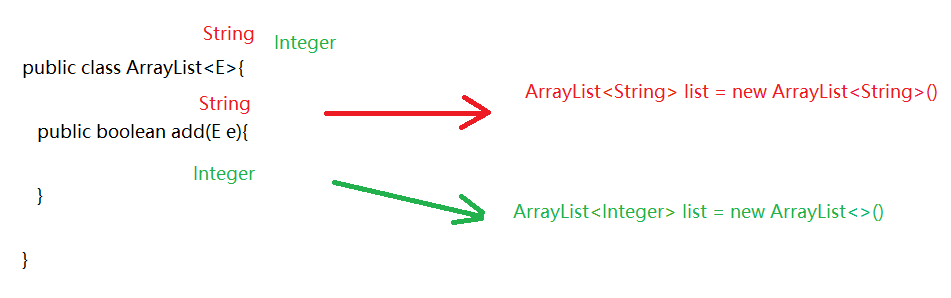
泛型 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. 泛型:<>2. 作用: 统一数据类型,防止将来的数据转换异常 3. 注意: a.泛型中的类型必须是引用类型 b.如果泛型不写,默认类型为Object
为什么要使用泛型 1 2 3 4 1. 从使用层面上来说: 统一数据类型,防止将来的数据类型转换异常 2. 从定义层面上来看: 定义带泛型的类,方法等,将来使用的时候给泛型确定什么类型,泛型就会变成什么类型,凡是涉及到泛型的都会变成确定的类型,代码更灵活
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo01Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList list = new ArrayList (); list.add("1" ); list.add(1 ); list.add("abc" ); list.add(2.5 ); list.add(true ); for (Object o : list) { String s = (String) o; System.out.println(s.length()); } } }
泛型的定义 含有泛型的类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 定义: public class 类名<E>{ } 2. 什么时候确定类型 new 对象的时候确定类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class MyArrayList <E>{ Object[] obj = new Object [10 ]; int size; public boolean add (E e) { obj[size] = e; size++; return true ; } public E get (int index) { return (E) obj[index]; } @Override public String toString () { return Arrays.toString(obj); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class Demo02Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { MyArrayList<String> list1 = new MyArrayList <>(); list1.add("aaa" ); list1.add("bbb" ); System.out.println(list1); System.out.println("===========" ); MyArrayList<Integer> list2 = new MyArrayList <>(); list2.add(1 ); list2.add(2 ); Integer element = list2.get(0 ); System.out.println(element); System.out.println(list2); } }
含有泛型的方法 1 2 3 4 5 1. 格式: 修饰符 <E> 返回值类型 方法名(E e) 2. 什么时候确定类型 调用的时候确定类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class ListUtils { public static <E> void addAll (ArrayList<E> list,E...e) { for (E element : e) { list.add(element); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class Demo03Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); ListUtils.addAll(list1,"a" ,"b" ,"c" ); System.out.println(list1); System.out.println("================" ); ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList <>(); ListUtils.addAll(list2,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ); System.out.println(list2); } }
含有泛型的接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 格式: public interface 接口名<E>{ } 2. 什么时候确定类型: a.在实现类的时候还没有确定类型,只能在new 实现类的时候确定类型了 ->比如 ArrayList b.在实现类的时候直接确定类型了 -> 比如Scanner
1 2 3 public interface MyList <E>{ public boolean add (E e) ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class MyArrayList1 <E> implements MyList <E>{ Object[] obj = new Object [10 ]; int size; public boolean add (E e) { obj[size] = e; size++; return true ; } public E get (int index) { return (E) obj[index]; } @Override public String toString () { return Arrays.toString(obj); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Demo04Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { MyArrayList1<String> list1 = new MyArrayList1 <>(); list1.add("张三" ); list1.add("李四" ); System.out.println(list1.get(0 )); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public interface MyIterator <E>{ E next () ; } public class MyScanner implements MyIterator <String>{ @Override public String next () { return "涛哥和金莲的故事" ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class Demo05Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { MyScanner myScanner = new MyScanner (); String result = myScanner.next(); System.out.println("result = " + result); } }
泛型的高级使用 泛型通配符 ? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Demo01Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); list1.add("张三" ); list1.add("李四" ); ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList <>(); list2.add(1 ); list2.add(2 ); method(list1); method(list2); } public static void method (ArrayList<?> list) { for (Object o : list) { System.out.println(o); } } }
泛型的上限下限 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 作用:可以规定泛型的范围2. 上限: a.格式:<? extends 类型> b.含义:?只能接收extends后面的本类类型以及子类类型 3. 下限: a.格式:<? super 类型> b.含义:?只能接收super 后面的本类类型以及父类类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Demo02Genericity { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<Number> list3 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<Object> list4 = new ArrayList <>(); get1(list1); get1(list3); System.out.println("=================" ); get2(list3); get2(list4); } public static void get1 (Collection<? extends Number> collection) { } public static void get2 (Collection<? super Number> collection) { } }
应用场景:
1.如果我们在定义类,方法,接口的时候,如果类型不确定,我们可以考虑定义含有泛型的类,方法,接口
2.如果类型不确定,但是能知道以后只能传递某个类的继承体系中的子类或者父类,就可以使用泛型的通配符
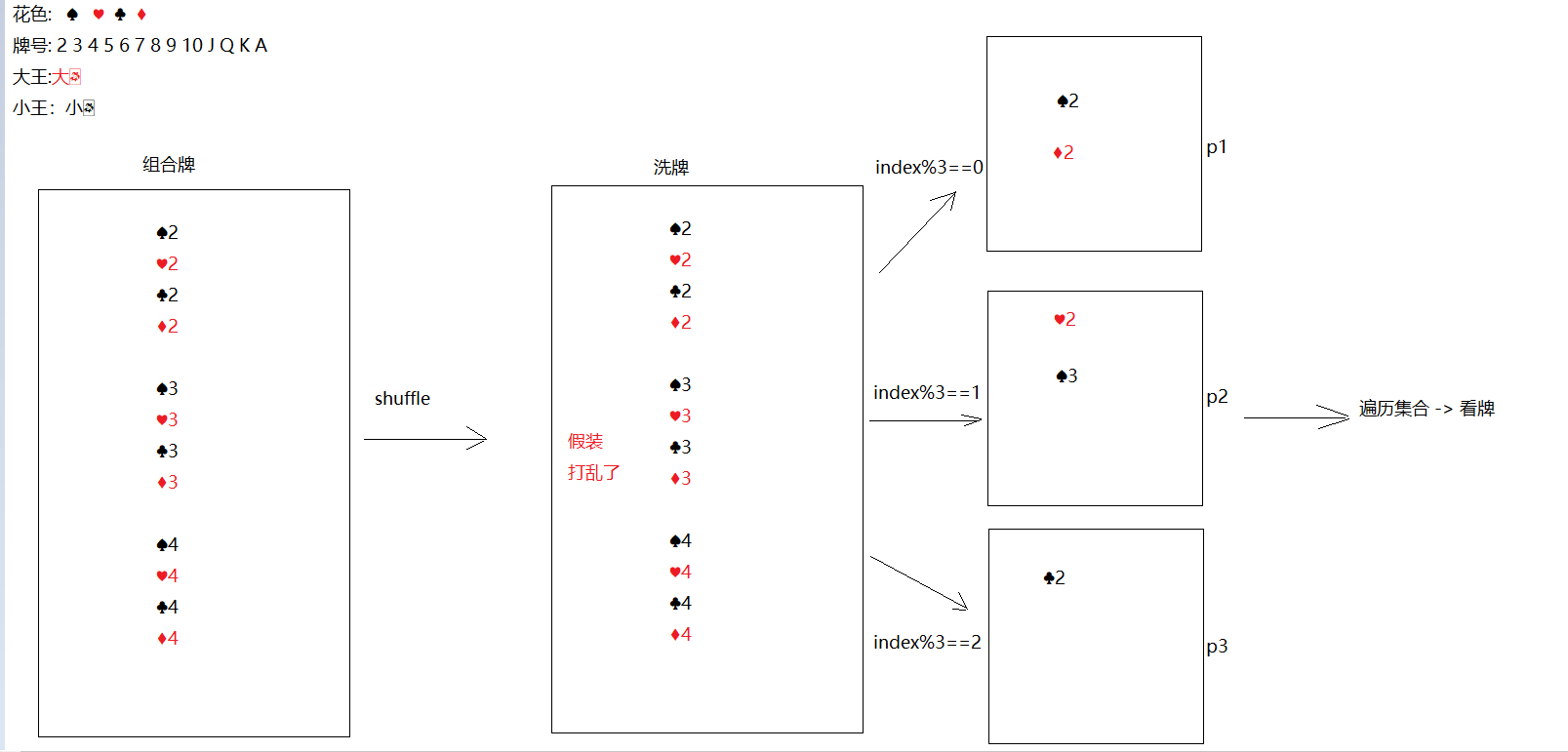
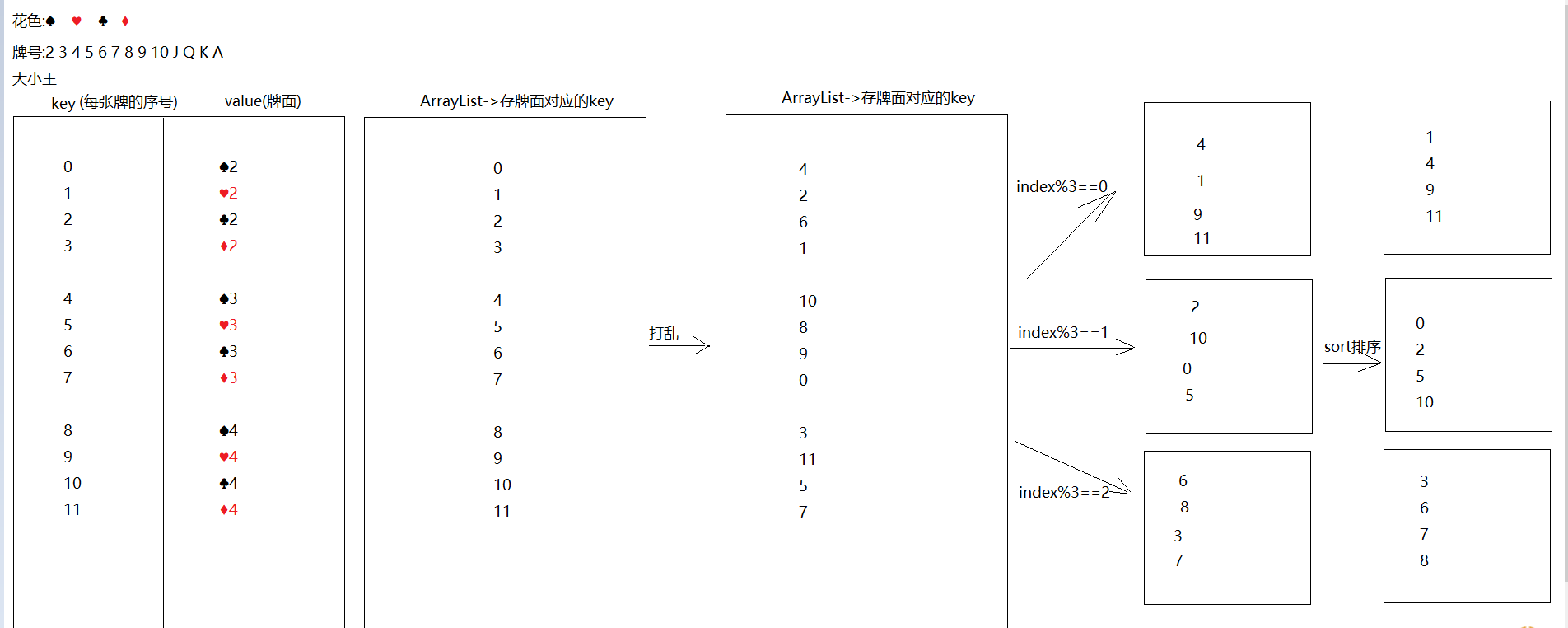
斗地主案例(扩展案例) 案例介绍 按照斗地主的规则,完成洗牌发牌的动作。
使用54张牌打乱顺序,三个玩家参与游戏,三人交替摸牌,每人17张牌,最后三张留作底牌。
案例分析 准备牌:
牌可以设计为一个ArrayList<String>,每个字符串为一张牌。
发牌:
将每个人以及底牌设计为ArrayList<String>,将最后3张牌直接存放于底牌,剩余牌通过对3取模依次发牌。
看牌:
直接打印每个集合。
代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. 创建ArrayList集合-> color -> 专门存花色2. 创建一个ArrayList集合 -> number -> 专门存牌号3. 创建一个ArrayList集合 -> poker -> 专门存花色和牌号组合好的牌面4. 打乱poker5. 创建4 个ArrayList集合,分别代表三个玩家,以及存储一个底牌6. 如果index为最后三张,往dipai集合中存7. 如果index%3 ==0 给p18. 如果index%3 ==1 给p29. 如果index%3 ==2 给p310. 遍历看牌
实现方式一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 public class Poker { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> color = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> number = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> poker = new ArrayList <>(); color.add("♠" ); color.add("♥" ); color.add("♣" ); color.add("♦" ); for (int i = 2 ; i <= 10 ; i++) { number.add(i + "" ); } number.add("J" ); number.add("Q" ); number.add("K" ); number.add("A" ); for (String num : number) { for (String huaSe : color) { String pokerNumber = huaSe + num; poker.add(pokerNumber); } } poker.add("😊" ); poker.add("☺" ); Collections.shuffle(poker); ArrayList<String> p1 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> p2 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> p3 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> dipai = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < poker.size(); i++) { String s = poker.get(i); if (i >= 51 ) { dipai.add(s); } else if (i % 3 == 0 ) { p1.add(s); } else if (i % 3 == 1 ) { p2.add(s); }else if (i%3 ==2 ){ p3.add(s); } } System.out.println("涛哥:" +p1); System.out.println("三上:" +p2); System.out.println("金莲:" +p3); System.out.println("底牌:" +dipai); } }
实现方式二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 public class Poker1 { public static void main (String[] args) { String[] color = "♠-♥-♣-♦" .split("-" ); String[] number = "2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-J-Q-K-A" .split("-" ); ArrayList<String> poker = new ArrayList <>(); for (String num : number) { for (String huaSe : color) { String pokerNumber = huaSe + num; poker.add(pokerNumber); } } poker.add("😊" ); poker.add("☺" ); Collections.shuffle(poker); ArrayList<String> p1 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> p2 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> p3 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<String> dipai = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < poker.size(); i++) { String s = poker.get(i); if (i >= 51 ) { dipai.add(s); } else if (i % 3 == 0 ) { p1.add(s); } else if (i % 3 == 1 ) { p2.add(s); }else if (i%3 ==2 ){ p3.add(s); } } System.out.println("涛哥:" +p1); System.out.println("三上:" +p2); System.out.println("金莲:" +p3); System.out.println("底牌:" +dipai); } }
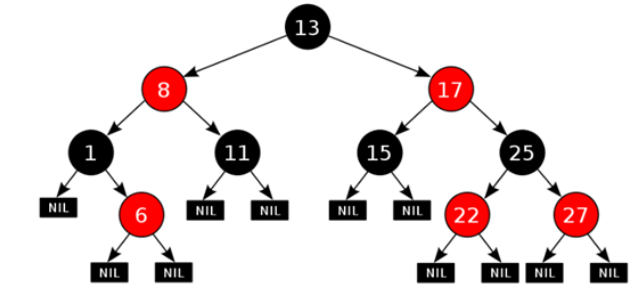
红黑树(了解) 1 2 3 4 5 集合加入红黑树的目的:提高查询效率 HashSet集合: 数据结构:哈希表 jdk8之前:哈希表 = 数组+链表 jdk8之后:哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树 ->为的是查询效率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. 每一个节点或是红色的,或者是黑色的2. 根节点必须是黑色3. 如果一个节点没有子节点或者父节点,则该节点相应的指针属性值为Nil,这些Nil视为叶节点,每个叶节点(Nil)是黑色的4. 如果某一个节点是红色,那么它的子节点必须是黑色(不能出现两个红色节点相连 的情况)5. 对每一个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点
红黑树结构插入数据在线演示: https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/RedBlack
Set集合 1 1. 涛哥总说:Set接口并没有对Collection接口进行功能上的扩充,而且所有的Set集合底层都是依靠Map实现
Set集合介绍 1 2 Set和Map密切相关的 Map的遍历需要先变成单列集合,只能变成set集合
HashSet集合的介绍和使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1. 概述:HashSet是Set接口的实现类2. 特点: a.元素唯一 b.元素无序 c.无索引 d.线程不安全 3. 数据结构:哈希表 a.jdk8之前:哈希表 = 数组+链表 b.jdk8之后:哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树 加入红黑树目的:查询快 4. 方法:和Collection一样5. 遍历: a.增强for b.迭代器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Demo01HashSet { public static void main (String[] args) { HashSet<String> set = new HashSet <>(); set.add("张三" ); set.add("李四" ); set.add("王五" ); set.add("赵六" ); set.add("田七" ); set.add("张三" ); System.out.println(set); Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("============" ); for (String s : set) { System.out.println(s); } } }
LinkedHashSet的介绍以及使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. 概述:LinkedHashSet extends HashSet 2. 特点: a.元素唯一 b.元素有序 c.无索引 d.线程不安全 3. 数据结构: 哈希表+双向链表 4. 使用:和HashSet一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Demo02LinkedHashSet { public static void main (String[] args) { LinkedHashSet<String> set = new LinkedHashSet <>(); set.add("张三" ); set.add("李四" ); set.add("王五" ); set.add("赵六" ); set.add("田七" ); set.add("张三" ); System.out.println(set); Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("============" ); for (String s : set) { System.out.println(s); } } }
哈希值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1. 概述:是由计算机算出来的一个十进制数,可以看做是对象的地址值2. 获取对象的哈希值,使用的是Object中的方法 public native int hashCode () 3. 注意:如果重写了hashCode方法,那计算的就是对象内容的哈希值了 4. 总结: a.哈希值不一样,内容肯定不一样 b.哈希值一样,内容也有可能不一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Person person = (Person) o; return Objects.equals(name, person.name) && Objects.equals(age, person.age); } @Override public int hashCode () { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Demo01Hash { public static void main (String[] args) { Person p1 = new Person ("涛哥" , 18 ); Person p2 = new Person ("涛哥" , 18 ); System.out.println(p1); System.out.println(p2); System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); System.out.println("======================" ); String s1 = "abc" ; String s2 = new String ("abc" ); System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); System.out.println(s2.hashCode()); System.out.println("=========================" ); String s3 = "通话" ; String s4 = "重地" ; System.out.println(s3.hashCode()); System.out.println(s4.hashCode()); } }
1 2 如果不重写hashCode方法,默认计算对象的哈希值 如果重写了hashCode方法,计算的是对象内容的哈希值
字符串的哈希值时如何算出来的 1 2 String s = "abc" byte [] value = {97 ,98 ,99 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public int hashCode () { int h = hash; if (h == 0 && !hashIsZero) { h = isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.hashCode(value) : StringUTF16.hashCode(value); if (h == 0 ) { hashIsZero = true ; } else { hash = h; } } return h; } ==================================================== StringLatin1.hashCode(value)底层源码,String中的哈希算法 public static int hashCode (byte [] value) { int h = 0 ; for (byte v : value) { h = 31 * h + (v & 0xff ); } return h; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 直接跑到StringLatin1.hashCode(value)底层源码,计算abc的哈希值-> 0xff 这个十六进制对应的十进制255 任何数据和255 做&运算,都是原值 第一圈: h = 31 *0 +97 = 97 第二圈: h = 31 *97 +98 = 3105 第三圈: h = 31 *3105 +99 = 96354
1 2 3 4 问题:在计算哈希值的时候,有一个定值就是31 ,为啥? 31 是一个质数,31 这个数通过大量的计算,统计,认为用31 ,可以尽量降低内容不一样但是哈希值一样的情况 内容不一样,哈希值一样(哈希冲突,哈希碰撞)
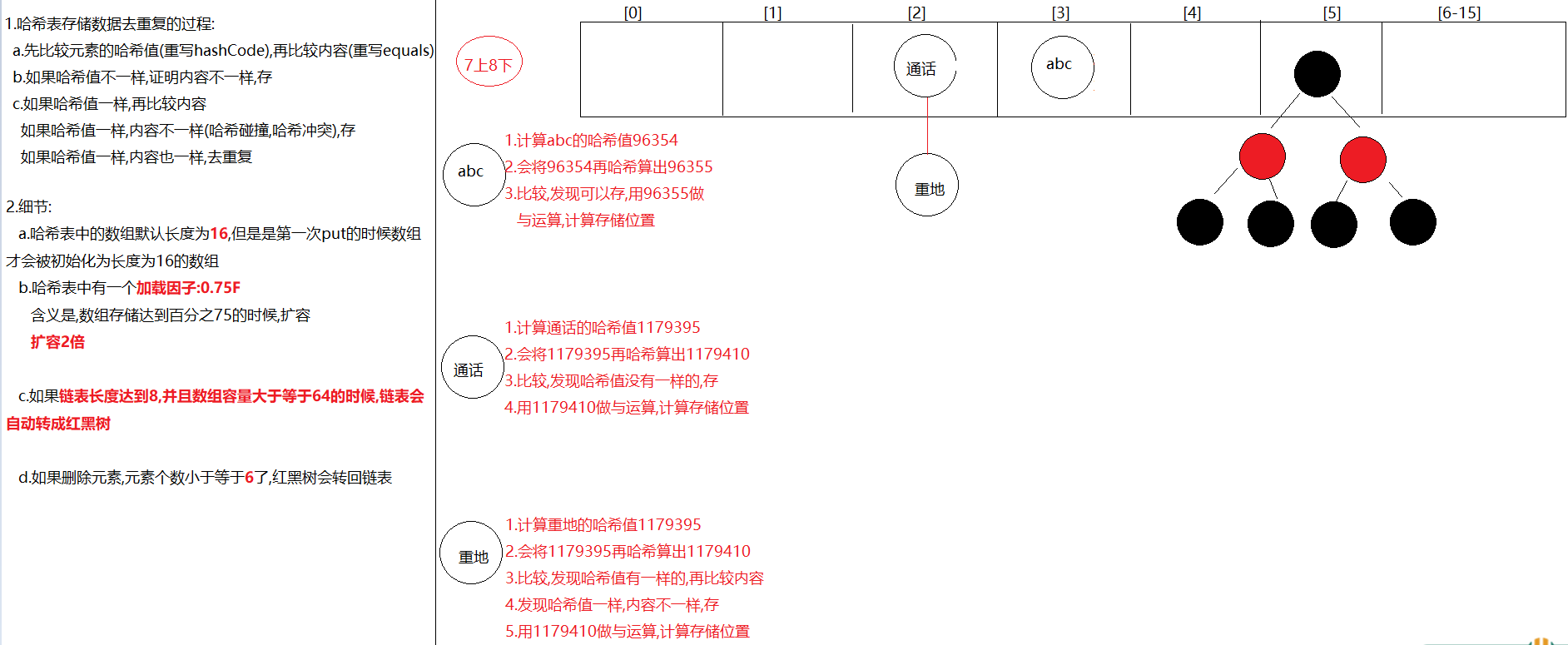
HashSet的存储去重复的过程 1 2 3 4 5 1. 先计算元素的哈希值(重写hashCode方法),再比较内容(重写equals方法)2. 先比较哈希值,如果哈希值不一样,存3. 如果哈希值一样,再比较内容 a.如果哈希值一样,内容不一样,存 b.如果哈希值一样,内容也一样,去重复
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { HashSet<String> set = new HashSet <>(); set.add("abc" ); set.add("通话" ); set.add("重地" ); set.add("abc" ); System.out.println(set); } }
HashSet存储自定义类型如何去重复 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Person person = (Person) o; return Objects.equals(name, person.name) && Objects.equals(age, person.age); } @Override public int hashCode () { return Objects.hash(name, age); } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Test03 { public static void main (String[] args) { HashSet<Person> set = new HashSet <>(); set.add(new Person ("涛哥" ,16 )); set.add(new Person ("金莲" ,24 )); set.add(new Person ("涛哥" ,16 )); System.out.println(set); } }
1 2 3 总结: 1. 如果HashSet存储自定义类型,如何去重复呢?重写hashCode和equals方法,让HashSet比较属性的哈希值以及属性的内容2. 如果不重写hashCode和equals方法,默认调用的是Object中的,不同的对象,肯定哈希值不一样,equals比较对象的地址值也不一样,所以此时即使对象的属性值一样,也不能去重复
模块十九总结及模块二十重点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 模块19回顾: 1.Collections集合工具类 方法: addAll-> 批量添加元素 shuffle-> 元素打乱 sort->排序-> ascii sort(集合,比较器)-> 按照指定的顺序排序 2.泛型: a.含有泛型的类: public class 类名<E>{} new对象的时候确定类型 b.含有泛型的方法: 修饰符 <E> 返回值类型 方法名(E e){} 调用的时候确定类型 c.含有泛型的接口 public interface 接口名<E>{} 在实现类的时候确定类型 在实现类的时候还没有确定类型,只能new对象的时候确定 d.泛型通配符 <? extends 类型> ?接收的泛型类型是后面类的本类以及子类 <? super 类型> ?接收的泛型类型是后面类的本类以及父类 3.哈希值:计算机计算出来的十进制数,可以看成是对象的地址值 a.要是没有重写hashCode方法,默认调用Object中的hashCode方法,计算的是对象的哈希值 b.要是重写了hashCode方法,计算的是对象内容的哈希值 4.HashSet集合 特点: 元素唯一 无序 无索引 线程不安全 数据结构: 哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树 5.LinkedHashSet 特点:元素唯一 有序 无索引 线程不安全 数据结构: 哈希表+双向链表 6.set存储自定义对象怎么去重复 -> 重写hashCode和equals方法 7.去重复过程:先比较元素哈希值,再比较内容 如果哈希值不一样,存 如果哈希值一样,再比较内容->哈希值一样,内容不一样,存;哈希值一样,内容一样,去重复 模块20重点: 1.会使用HashMap和LinkedHashMap以及知道他们的特点 2.会使用Properties属性集 3.会操作集合嵌套 4.知道哈希表结构存储元素过程
Map集合
Map的介绍 1 2 3 1. 概述:是双列集合的顶级接口2. 元素特点: 元素都是由key(键),value(值)组成 -> 键值对
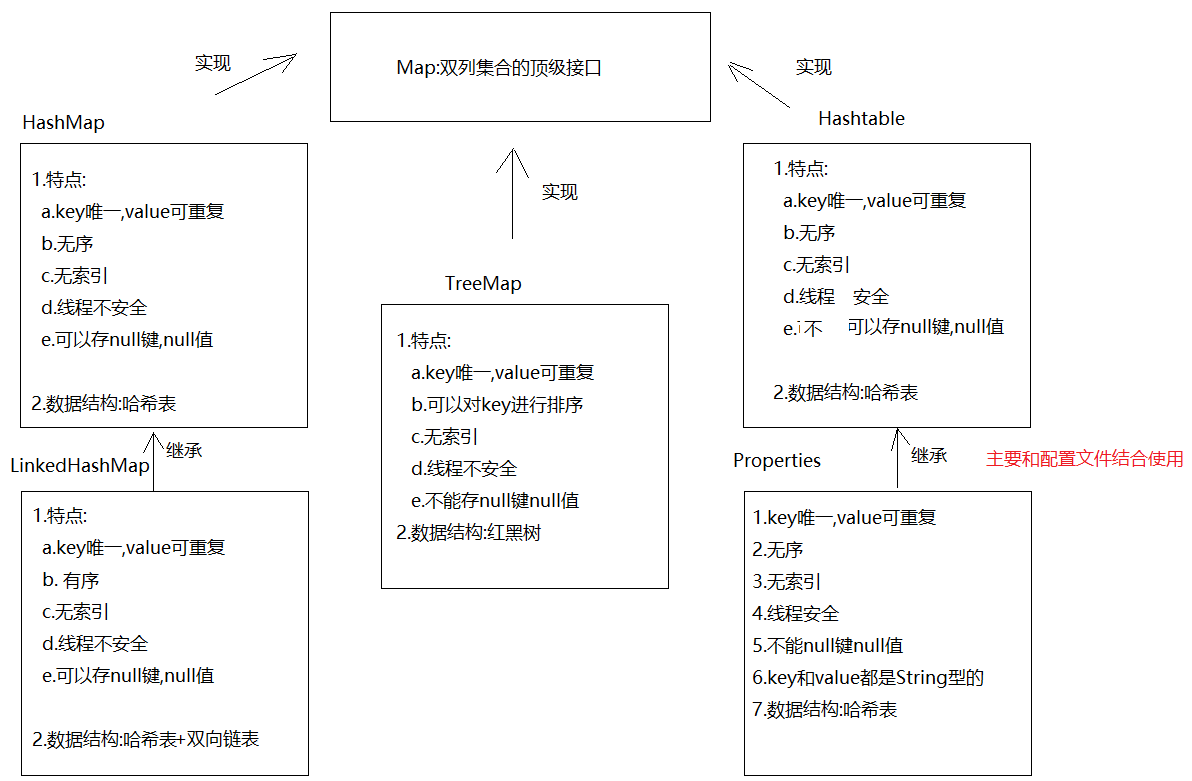
HashMap的介绍和使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 1. 概述:HashMap是Map的实现类2. 特点: a.key唯一,value可重复 -> 如果key重复了,会发生value覆盖 b.无序 c.无索引 d.线程不安全 e.可以存null 键null 值 3. 数据结构: 哈希表 4. 方法: V put (K key, V value) -> 添加元素,返回的是 V remove (Object key) ->根据key删除键值对,返回的是被删除的value V get (Object key) -> 根据key获取value boolean containsKey (Object key) -> 判断集合中是否包含指定的key Collection<V> values () -> 获取集合中所有的value,转存到Collection集合中 Set<K> keySet () ->将Map中的key获取出来,转存到Set集合中 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()->获取Map集合中的键值对,转存到Set集合中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Demo01HashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap <>(); String value1 = map.put("猪八" , "嫦娥" ); System.out.println(value1); String value2 = map.put("猪八" , "高翠兰" ); System.out.println(value2); System.out.println(map); map.put("后裔" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("二郎神" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("唐僧" ,"女儿国国王" ); map.put("涛哥" ,"金莲" ); map.put(null ,null ); System.out.println(map); String value3 = map.remove("涛哥" ); System.out.println(value3); System.out.println(map); System.out.println(map.get("唐僧" )); System.out.println(map.containsKey("二郎神" )); Collection<String> collection = map.values(); System.out.println(collection); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. 概述:LinkedHashMap extends HashMap 2. 特点: a.key唯一,value可重复 -> 如果key重复了,会发生value覆盖 b.有序 c.无索引 d.线程不安全 e.可以存null 键null 值 3. 数据结构: 哈希表+双向链表 4. 使用:和HashMap一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo02LinkedHashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); map.put("八戒" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("涛哥" ,"金莲" ); map.put("涛哥" ,"三上" ); map.put("唐僧" ,"女儿国国王" ); System.out.println(map); } }
HashMap的两种遍历方式 方式一: 获取key,根据key再获取value 1 Set<K> keySet () ->将Map中的key获取出来,转存到Set集合中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Demo03HashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("猪八" , "嫦娥" ); map.put("猪八" , "高翠兰" ); map.put("后裔" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("二郎神" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("唐僧" ,"女儿国国王" ); map.put("涛哥" ,"金莲" ); Set<String> set = map.keySet(); for (String key : set) { System.out.println(key+".." +map.get(key)); } } }
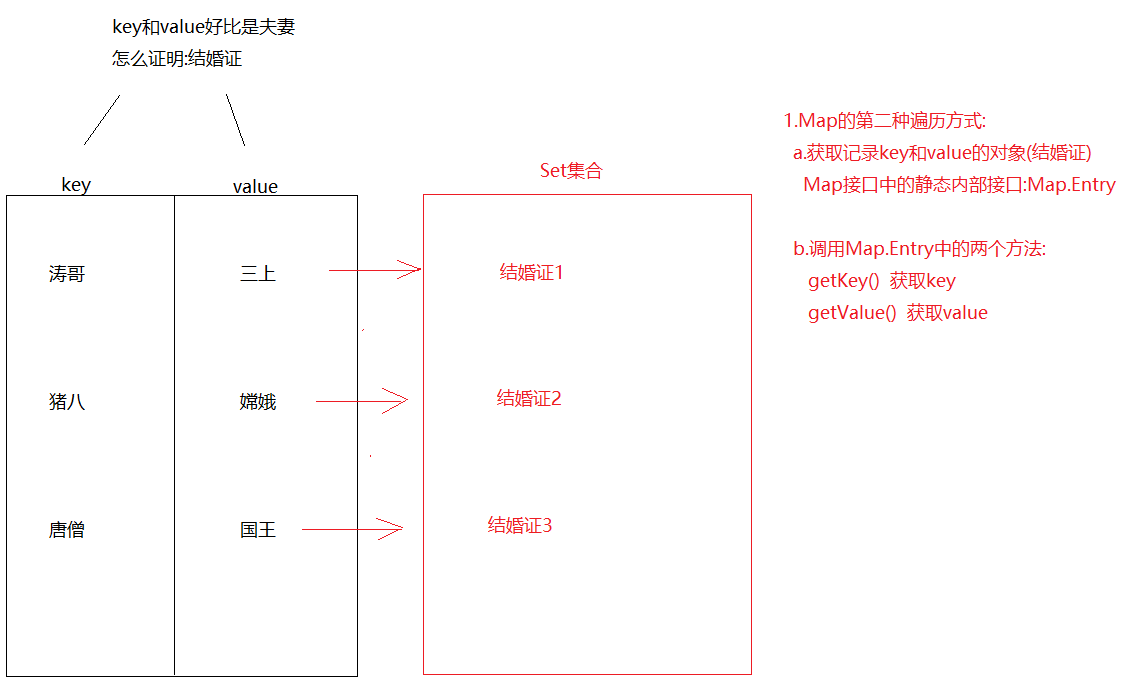
方式二: 同时获取key和value
1 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()->获取Map集合中的键值对,转存到Set集合中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Demo04HashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("猪八" , "嫦娥" ); map.put("猪八" , "高翠兰" ); map.put("后裔" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("二郎神" ,"嫦娥" ); map.put("唐僧" ,"女儿国国王" ); map.put("涛哥" ,"金莲" ); Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : set) { String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"..." +value); } } }
Map存储自定义对象时如何去重复 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Person person = (Person) o; return Objects.equals(name, person.name) && Objects.equals(age, person.age); } @Override public int hashCode () { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class Demo05HashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<Person, String> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put(new Person ("涛哥" ,18 ),"河北省" ); map.put(new Person ("三上" ,26 ),"日本" ); map.put(new Person ("涛哥" ,18 ),"北京市" ); System.out.println(map); } }
1 2 如果key为自定义类型,去重复的话,重写hashCode和equals方法,去重复过程和set一样一样的 因为set集合的元素到了底层都是保存到了map的key位置上
Map的练习 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 需求:用Map集合统计字符串中每一个字符出现的次数 步骤: 1. 创建Scanner和HashMap 2. 遍历字符串,将每一个字符获取出来 3. 判断,map中是否包含遍历出来的字符 -> containsKey 4. 如果不包含,证明此字符第一次出现,直接将此字符和1 存储到map中 5. 如果包含,根据字符获取对应的value,让value++ 6. 将此字符和改变后的value重新保存到map集合中 7. 输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class Demo06HashMap { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); String data = sc.next(); char [] chars = data.toCharArray(); for (char aChar : chars) { String key = aChar+"" ; if (!map.containsKey(key)){ map.put(key,1 ); }else { Integer value = map.get(key); value++; map.put(key,value); } } System.out.println(map); } }
斗地主Map版本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 public class Demo07Poker { public static void main (String[] args) { String[] color = "♠-♥-♣-♦" .split("-" ); String[] number = "2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-J-Q-K-A" .split("-" ); HashMap<Integer, String> poker = new HashMap <>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(0 ); list.add(1 ); int key = 2 ; for (String num : number) { for (String huaSe : color) { String pokerNumber = huaSe+num; poker.put(key,pokerNumber); list.add(key); key++; } } poker.put(0 ,"😊" ); poker.put(1 ,"☺" ); Collections.shuffle(list); ArrayList<Integer> p1 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<Integer> p2 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<Integer> p3 = new ArrayList <>(); ArrayList<Integer> dipai = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { Integer key1 = list.get(i); if (i>=51 ){ dipai.add(key1); }else if (i%3 ==0 ){ p1.add(key1); }else if (i%3 ==1 ){ p2.add(key1); }else if (i%3 ==2 ){ p3.add(key1); } } Collections.sort(p1); Collections.sort(p2); Collections.sort(p3); Collections.sort(dipai); lookPoker("涛哥" ,p1,poker); lookPoker("三上" ,p2,poker); lookPoker("金莲" ,p3,poker); lookPoker("大郎" ,dipai,poker); } private static void lookPoker (String name, ArrayList<Integer> list, HashMap<Integer, String> map) { System.out.print(name+":" ); for (Integer key : list) { String value = map.get(key); System.out.print(value+" " ); } System.out.println(); } }
哈希表结构存储过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1. HashMap底层数据数据结构:哈希表2. jdk7:哈希表 = 数组+链表 jdk8:哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树 3. 先算哈希值,此哈希值在HashMap底层经过了特殊的计算得出 如果哈希值不一样,直接存 如果哈希值一样,再去比较内容,如果内容不一样,也存 如果哈希值一样,内容也一样,直接去重复(后面的value将前面的value覆盖) 哈希值一样,内容不一样->哈希冲突(哈希碰撞) 4. 要知道的点: a.在不指定长度时,哈希表中的数组默认长度为16 ,HashMap创建出来,一开始没有创建长度为16 的数组 b.什么时候创建的长度为16 的数组呢?在第一次put的时候,底层会创建长度为16 的数组 c.哈希表中有一个数据加[加载因子]->默认为0.75 (加载因子)->代表当元素存储到百分之75 的时候要扩容了->2 倍 d.如果对个元素出现了哈希值一样,内容不一样时,就会在同一个索引上以链表的形式存储,当链表长度达到8 并且当前数组长度>=64 时,链表就会改成使用红黑树存储 如果后续删除元素,那么在同一个索引位置上的元素个数小于6 ,红黑树会变回链表 e.加入红黑树目的:查询快
1 2 3 4 5 6 外面笔试时可能会问到的变量 default_initial_capacity:HashMap默认容量 16 default_load_factor:HashMap默认加载因子 0.75f threshold:扩容的临界值 等于 容量*0.75 = 12 第一次扩容 treeify_threshold:链表长度默认值,转为红黑树:8 min_treeify_capacity:链表被树化时最小的数组容量:64
1.问题: 哈希表中有数组的存在,但是为啥说没有索引呢?
哈希表中虽然有数组,但是set和map却没有索引,因为存数据的时候有可能在同一个索引下形成链表,如果2索引上有一条链表,那么我们要是按照索引2获取,咱们获取哪个元素呢?所以就取消了按照索引操作的机制
2.问题:为啥说HashMap是无序的,LinkedHashMap是有序的呢?
原因:HashMap底层哈希表为单向链表
LinkedHashMap底层在哈希表的基础上加了一条双向链表
HashMap无参数构造方法的分析 1 2 3 4 5 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f ;public HashMap () { this .loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; }
解析:使用无参数构造方法创建HashMap对象,将加载因子设置为默认的加载因子,loadFactor=0.75F。
HashMap有参数构造方法分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) ->创建Map集合的时候指定底层数组长度以及加载因子 public HashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this .loadFactor = loadFactor; this .threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); }
解析:带有参数构造方法,传递哈希表的初始化容量和加载因子
如果initialCapacity(初始化容量)小于0,直接抛出异常。
如果initialCapacity大于最大容器,initialCapacity直接等于最大容器
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30 是最大容量 (1073741824)
如果loadFactor(加载因子)小于等于0,直接抛出异常
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity)方法计算哈希表的初始化容量。
注意:哈希表是进行计算得出的容量,而初始化容量不直接等于我们传递的参数。
tableSizeFor方法分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static final int tableSizeFor (int cap) { int n = cap - 1 ; n |= n >>> 1 ; n |= n >>> 2 ; n |= n >>> 4 ; n |= n >>> 8 ; n |= n >>> 16 ; return (n < 0 ) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1 ; } 8 4 2 1 规则->无论指定了多少容量,最终经过tableSizeFor这个方法计算之后,都会遵循8421 规则去初始化列表容量为了存取高效,尽量较少碰撞
解析:该方法对我们传递的初始化容量进行位移运算,位移的结果是 8 4 2 1 码
例如传递2,结果还是2,传递的是4,结果还是4。
例如传递3,结果是4,传递5,结果是8,传递20,结果是32。
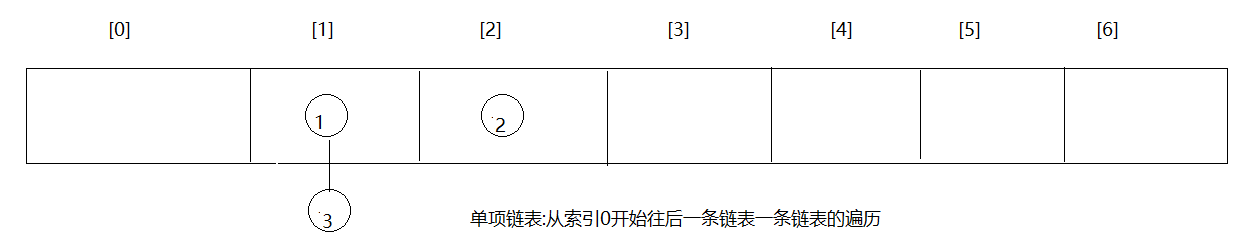
Node 内部类分析 哈希表是采用数组+链表的实现方法,HashMap中的内部类Node非常重要,证明HashSet是一个单向链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static class Node <K,V> implements Map .Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next; }
解析:内部类Node中具有4个成员变量
hash,对象的哈希值
key,作为键的对象
value,作为值得对象(讲解Set集合,不牵扯值得问题)
next,下一个节点对象
存储元素的put方法源码 1 2 3 public V put (K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true ); }
解析:put方法中调研putVal方法,putVal方法中调用hash方法。
hash(key)方法:传递要存储的元素,获取对象的哈希值
putVal方法,传递对象哈希值和要存储的对象key
putVal方法源码 1 2 3 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) n = (tab = resize()).length;
解析:方法中进行Node对象数组的判断,如果数组是null或者长度等于0,那么就会调研resize()方法进行数组的扩容。
resize方法的扩容计算 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (oldCap > 0 ) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1 ) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1 ; }
解析:计算结果,新的数组容量=原始数组容量<<1,也就是乘以2。
确定元素存储的索引 1 2 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1 ) & hash]) == null ) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null );
解析:i = (数组长度 - 1) & 对象的哈希值,会得到一个索引,然后在此索引下tab[i],创建链表对象。
不同哈希值的对象,也是有可能存储在同一个数组索引下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 其中resize()扩容的方法,默认是16 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null );->将元素放在数组中 i就是索引 i = (n - 1 ) & hash 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 ->15 & 0 &0 =0 0 &1 =0 1 &1 =1 0000 0000 0000 0001 0111 1000 0110 0011 ->96355 -------------------------------------------------------- 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 ->3
1 2 3 4 5 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 ->15 & 0 &0 =0 0 &1 =0 1 &1 =1 0000 0000 0001 0001 1111 1111 0001 0010 ->1179410 -------------------------------------------------------- 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 ->2
遇到重复哈希值的对象 1 2 3 4 Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p;
解析:如果对象的哈希值相同,对象的equals方法返回true,判断为一个对象,进行覆盖操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 else { for (int binCount = 0 ; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null ) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1 ) treeifyBin(tab, hash); break ; }
解析:如果对象哈希值相同,但是对象的equals方法返回false,将对此链表进行遍历,当链表没有下一个节点的时候,创建下一个节点存储对象.
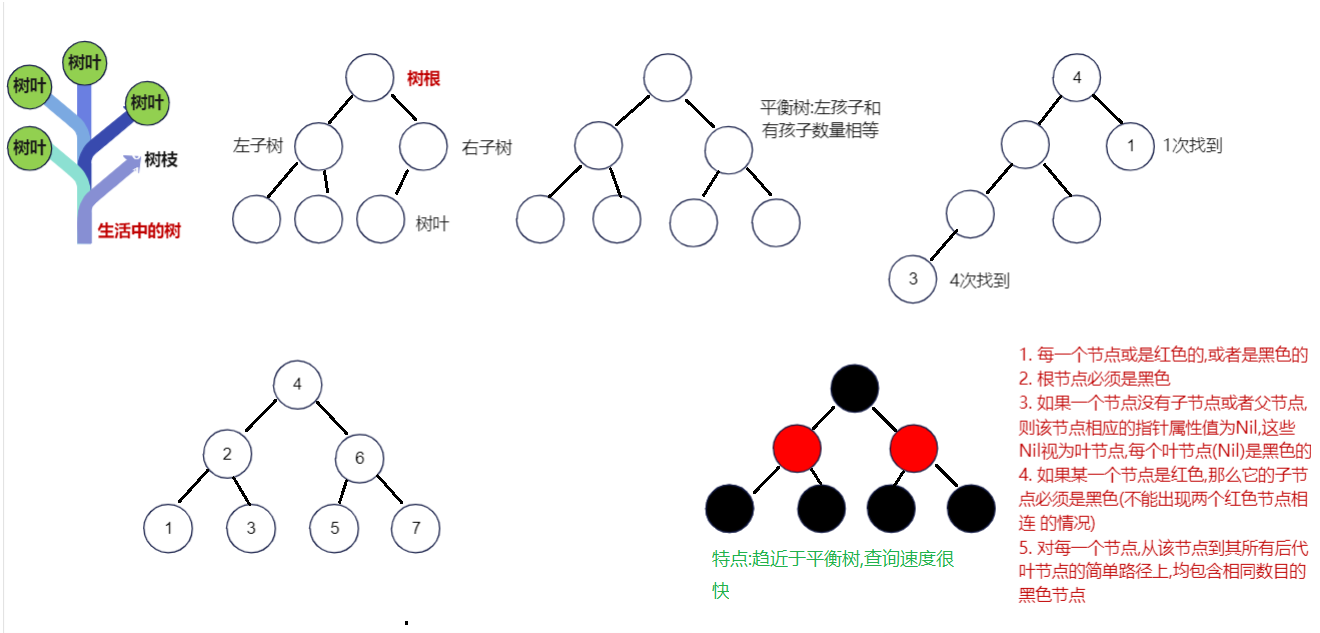
TreeSet 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. 概述:TreeSet是Set的实现类2. 特点: a.对元素进行排序 b.无索引 c.不能存null d.线程不安全 e.元素唯一 3. 数据结构:红黑树
1 2 3 构造: TreeSet() -> 构造一个新的空 set,该 set 根据其元素的自然顺序进行排序 -> ASCII TreeSet (Comparator<? super E> comparator) 构造一个新的空 TreeSet,它根据指定比较器进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Person person = (Person) o; return Objects.equals(name, person.name) && Objects.equals(age, person.age); } @Override public int hashCode () { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Demo01TreeSet { public static void main (String[] args) { TreeSet<String> set1 = new TreeSet <>(); set1.add("c.白毛浮绿水" ); set1.add("a.鹅鹅鹅" ); set1.add("b.曲项向天歌" ); set1.add("d.红掌拨清波" ); System.out.println(set1); System.out.println("=====================" ); TreeSet<Person> set2 = new TreeSet <>(new Comparator <Person>() { @Override public int compare (Person o1, Person o2) { return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge(); } }); set2.add(new Person ("柳岩" ,18 )); set2.add(new Person ("涛哥" ,12 )); set2.add(new Person ("三上" ,20 )); System.out.println(set2); } }
TreeMap 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. 概述:TreeMap是Map的实现类2. 特点: a.对key进行排序 b.无索引 c.key唯一 d.线程不安全 e.不能存null 3. 数据结构:红黑树
1 2 3 构造: TreeMap() -> 使用键的自然顺序构造一个新的、空的树映射 -> ASCII TreeMap (Comparator<? super E> comparator) 构造一个新的、空的树映射,该映射根据给定比较器进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person () { } public Person (String name, Integer age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } @Override public String toString () { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) return true ; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false ; Person person = (Person) o; return Objects.equals(name, person.name) && Objects.equals(age, person.age); } @Override public int hashCode () { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Demo02TreeMap { public static void main (String[] args) { TreeMap<String, String> map1 = new TreeMap <>(); map1.put("c" ,"白毛浮绿水" ); map1.put("a" ,"鹅鹅鹅" ); map1.put("b" ,"曲项向天歌" ); map1.put("d" ,"红掌拨清波" ); System.out.println(map1); System.out.println("=============" ); TreeMap<Person, String> map2 = new TreeMap <>(new Comparator <Person>() { @Override public int compare (Person o1, Person o2) { return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge(); } }); map2.put(new Person ("柳岩" ,18 ),"北京" ); map2.put(new Person ("涛哥" ,12 ),"北京" ); map2.put(new Person ("三上" ,20 ),"北京" ); System.out.println(map2); } }
Hashtable和Vector集合(了解) Hashtable集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. 概述:Hashtable是Map的实现类2. 特点: a.key唯一,value可重复 b.无序 c.无索引 d.线程安全 e.不能存储null 键,null 值 3. 数据结构:哈希表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Demo01Hashtable { public static void main (String[] args) { Hashtable<String, String> table = new Hashtable <>(); table.put("迪丽热巴" ,"马尔扎哈" ); table.put("古力娜扎" ,"涛哥思密达" ); table.put("古力娜扎" ,"雷霆嘎巴" ); table.put("玛卡巴卡" ,"哈哈哈哈" ); System.out.println(table); } }
HashMap和Hashtable区别:
相同点:元素无序,无索引,key唯一
不同点:HashMap线程不安全,Hashtable线程安全
HashMap可以存储null键null值;Hashtable不能
Vector集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. 概述:Vector是List接口的实现类2. 特点: a.元素有序 b.有索引 c.元素可重复 d.线程安全 3. 数据结构:数组 4. 源码分析: a.如果用空参构造创建对象,数组初始容量为10 ,如果超出范围,自动扩容,2 倍 b.如果用有参构造创建对象,如果超出了范围,自动扩容,扩的是老数组长度+指定的容量增强
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo02Vector { public static void main (String[] args) { Vector<String> vector = new Vector <>(); vector.add("张三" ); vector.add("李四" ); for (String s : vector) { System.out.println(s); } } }
Vector底层源码分析
1 2 Vector() 构造一个空向量,使其内部数据数组的大小为 10 ,其标准容量增量为零 Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)使用指定的初始容量和容量增量构造一个空的向量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 Vector<String> vector = new Vector <>(); public Vector () { this (10 ); } public Vector (int initialCapacity->10 ) { this (initialCapacity, 0 ); } public Vector (int initialCapacity->10 , int capacityIncrement->0 ) { super (); if (initialCapacity < 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; this .capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement; } ===================================================== vector.add("李四" );-> 假设李四是第11 个元素 public synchronized boolean add (E e) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1 ); elementData[elementCount++] = e; return true ; } private void ensureCapacityHelper (int minCapacity->11 ) { if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity->11 ); } private void grow (int minCapacity->11 ) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0 ) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Vector<String> vector = new Vector <>(10 ,5 ); public Vector (int initialCapacity->10 , int capacityIncrement->5 ) { super (); if (initialCapacity < 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; this .capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement; } ====================================================== vector.add("李四" );-> 假设李四是第11 个元素 public synchronized boolean add (E e) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1 ); elementData[elementCount++] = e; return true ; } private void ensureCapacityHelper (int minCapacity->11 ) { if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity->11 ) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0 ) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
Properties集合(属性集) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1. 概述:Properties 继承自 Hashtable2. 特点: a.key唯一,value可重复 b.无序 c.无索引 d.线程安全 e.不能存null 键,null 值 f.Properties的key和value类型默认为String 3. 数据结构:哈希表4. 特有方法: Object setProperty (String key, String value) -> 存键值对 String getProperty (String key) ->根据key获取value的 Set<String> stringPropertyNames () -> 获取所有的key,保存到set集合中,相当于keySet方法 void load (InputStream inStream) -> 将流中的数据加载到Properties集合中(IO部分讲)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Demo01Properties { public static void main (String[] args) { Properties properties = new Properties (); properties.setProperty("username" ,"root" ); properties.setProperty("password" ,"1234" ); System.out.println(properties); System.out.println(properties.getProperty("username" )); Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames(); for (String key : set) { System.out.println(properties.getProperty(key)); } } }
集合嵌套 List嵌套List 1 需求:创建2 个List集合,每个集合中分别存储一些字符串,将2 个集合存储到第3 个List集合中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Demo01ListInList { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); list1.add("杨过" ); list1.add("小龙女" ); list1.add("尹志平" ); ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList <>(); list2.add("涛哥" ); list2.add("金莲" ); list2.add("三上" ); ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(list1); list.add(list2); for (ArrayList<String> arrayList : list) { for (String s : arrayList) { System.out.println(s); } } } }
List嵌套Map 1 1 班级有第三名同学,学号和姓名分别为:1 =张三,2 =李四,3 =王五,2 班有三名同学,学号和姓名分别为:1 =黄晓明,2 =杨颖,3 =刘德华,请将同学的信息以键值对的形式存储到2 个Map集合中,在将2 个Map集合存储到List集合中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class Demo02ListInMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<Integer, String> map1 = new HashMap <>(); map1.put(1 ,"张三" ); map1.put(2 ,"李四" ); map1.put(3 ,"王五" ); HashMap<Integer, String> map2 = new HashMap <>(); map2.put(1 ,"黄晓明" ); map2.put(2 ,"杨颖" ); map2.put(3 ,"刘德华" ); ArrayList<HashMap<Integer, String>> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(map1); list.add(map2); for (HashMap<Integer, String> map : list) { Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : set) { System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"..." +entry.getValue()); } } } }
Map嵌套Map 1 2 3 4 5 6 - JavaSE 集合 存储的是 学号 键,值学生姓名 - 1 张三 - 2 李四 - JavaEE 集合 存储的是 学号 键,值学生姓名 - 1 王五 - 2 赵六
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Demo03MapInMap { public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<Integer, String> map1 = new HashMap <>(); map1.put(1 ,"张三" ); map1.put(2 ,"李四" ); HashMap<Integer, String> map2 = new HashMap <>(); map2.put(1 ,"王五" ); map2.put(2 ,"赵六" ); HashMap<String, HashMap<Integer, String>> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("javase" ,map1); map.put("javaee" ,map2); Set<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Integer, String>>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Integer, String>> entry : set) { HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = entry.getValue(); Set<Integer> set1 = hashMap.keySet(); for (Integer key : set1) { System.out.println(key+"..." +hashMap.get(key)); } } } }
模块二十总结 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 模块20回顾: 1.HashMap a.特点:无序,无索引,key唯一,线程不安全,可以存null键null值 b.数据结构:哈希表 c.方法:put remove get keySet entrySet values containsKey 2.LinkedHashMap: a.特点:有序,无索引,key唯一,线程不安全,可以存null键null值 b.数据结构:哈希表+双向链表 3.key如何去重复:重写hashCode和equals方法 4.TreeSet:是set接口实现类 a.特点:对元素排序,无索引,元素唯一,线程不安全,不可以存null键null值 b.构造: TreeSet() TreeSet(Comparator c) 5.TreeMap: a.特点:对 key排序,无索引,key唯一,线程不安全,不可以存null键null值 b.构造: TreeMap() TreeMap(Comparator c) 6.Hashtable:是map接口的实现类 a.特点:无序,无索引,key唯一,线程安全,不能存null键null值 b.用法:和HashMap一样 c.数据结构:哈希表 7.Vector: a.特点:有序,有索引,元素可重复,线程安全 b.数据结构:数组 8.Properties:是Hashtable子类 a.特点:无序,无索引,key唯一,线程安全,不能存null键null值,key和value都是String的 b.特有方法: setProperty getProperty stringPropertyNames load(IO流对象) -> 将流中数据加载到集合中